Analyze with AI
Get AI-powered insights from this Mad Devs article:
Any entrepreneur who wants to start an online business or an existing company that wants to scale will benefit from the various cloud computing solutions available today. This may include saving money and space by using public clouds, protecting sensitive data with private clouds, or combining both approaches. Leaders who want to maximize their business's profits need to understand the nuances of the different delivery and service models in cloud solutions.
This article will explore these models with a close look at their applications and the benefits they deliver as well as the challenges of their implementation.
The details of cloud computing for business
Cloud computing is a technology that uses remote servers on the Internet to store, manage, and access data online rather than through local computing (on-premise infrastructure) in server rooms. The concept is to provide convenient, on-demand access with little management effort or provider interaction. To be classified under cloud computing, services must meet these criteria:
- On-demand self-service
- Broad network access
- Resource pooling
- Rapid elasticity
- Pay-as-you-go model
Cloud computing demonstrates these characteristics in the form of various services that match the different needs of customers, such as:
- Software as a service (SaaS)
- Platform as a service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
- Anything/Everything as a service (XaaS)
- Function as a Service (FaaS)
Despite their common characteristics, cloud networks differ in how they are delivered. There are four models for delivering cloud solutions:
Each service and delivery model involves separate aspects that require a thorough explanation to understand the advantages and disadvantages of applying them in different companies.
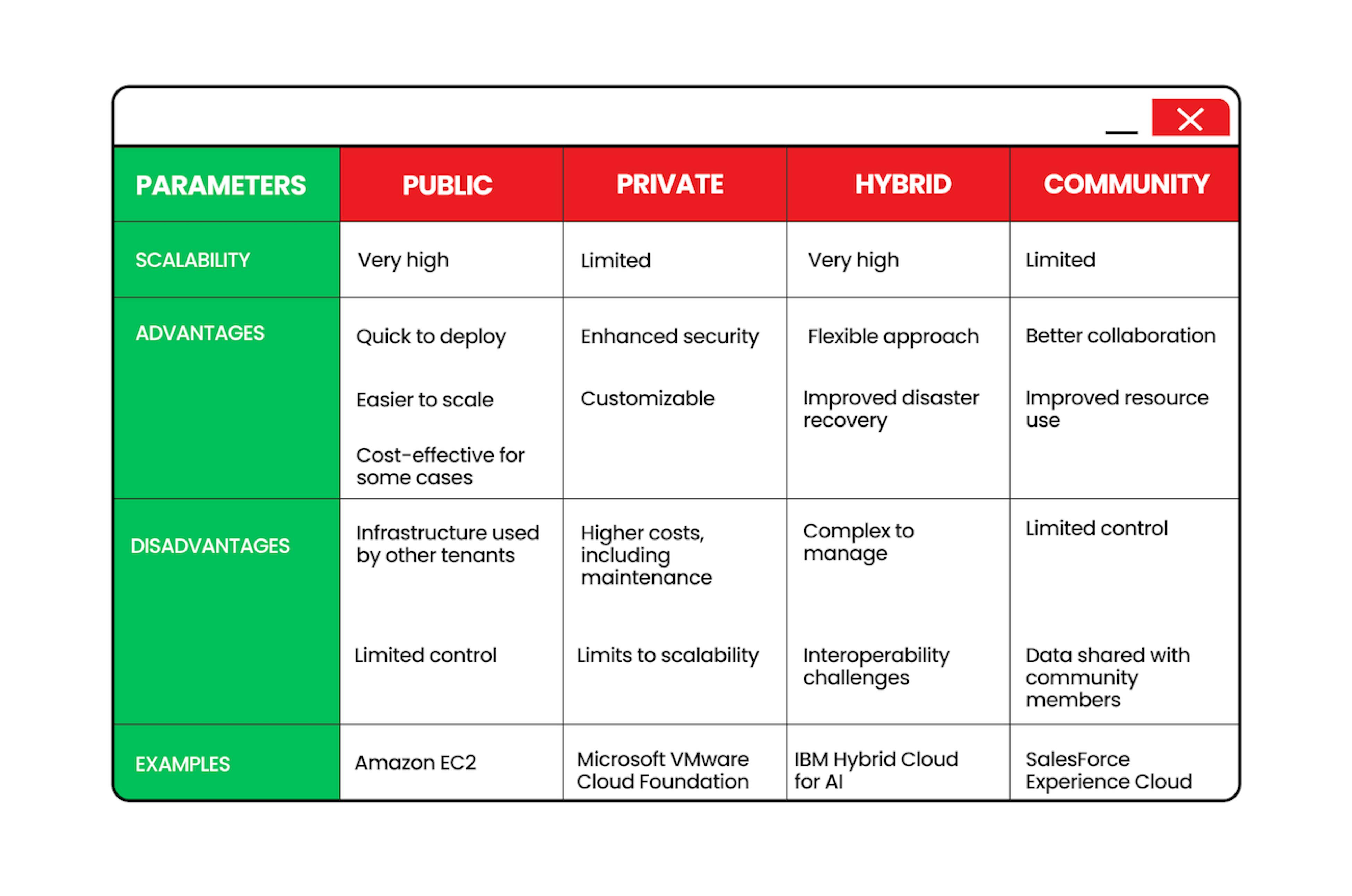
4 types of cloud deployment models
Cloud deployment models refer to the cloud infrastructure's location and who has access to it. The four primary models are Public, Private, Hybrid, and Community, and they vary in terms of their complexity and security.
Public cloud
Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party providers and are available to the general public. These deployments are typically housed on public servers accessible over the internet or through a VPN service, and the service owner typically owns the hardware and software used in these facilities. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
➕ Advantages
- Cost-effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go pricing and on-demand provisioning make public clouds highly cost-effective for businesses with certain workloads and timeframes.
- Scalability and flexibility: Easily scale resources up or down to meet fluctuating demands and ensure optimal performance and cost efficiency.
- Wide range of services: Public cloud providers offer a vast array of services that include computing, storage, networking, databases, and analytics.
➖ Disadvantages
- Security concerns: Data security and privacy can be a concern in public clouds, as the infrastructure is shared with other tenants, which increases attack vectors.
- Limited control: Users have limited control over the underlying infrastructure and may be subject to service limitations or disruptions.
- Vendor lock-in: Migrating to a different public cloud provider can be challenging due to vendor-specific technologies and data dependencies.
Private cloud
Private clouds are dedicated to a single organization or a group of organizations with shared concerns. In many cases, these clouds are created and managed by the company's staff in an on-premise configuration. However, there are third-party providers of private clouds that deploy cloud services for other businesses. In either case, ownership of these services is the most crucial element. Public users and those not associated with the organization can't access the platform. Medical organizations and banking institutions are examples of organizations that can benefit from a private cloud infrastructure.
➕ Advantages
- Enhanced security and control: Private clouds offer enhanced security and control over data and infrastructure, as they are isolated from other tenants.
- Customization and flexibility: Organizations have greater control over customization and configuration to allow for tailored solutions.
- Compliance: Private clouds can be more easily configured to comply with industry regulations and data privacy requirements.
➖ Disadvantages
- Higher costs: Private clouds can be more expensive to deploy and maintain compared to public clouds and require significant upfront investment.
- Limited scalability: Scaling resources in a private cloud can be more challenging depending on a company's resources and personnel's skill sets.
- Higher maintenance overhead: Organizations are responsible for managing and maintaining the entire infrastructure: hardware, software, and security.
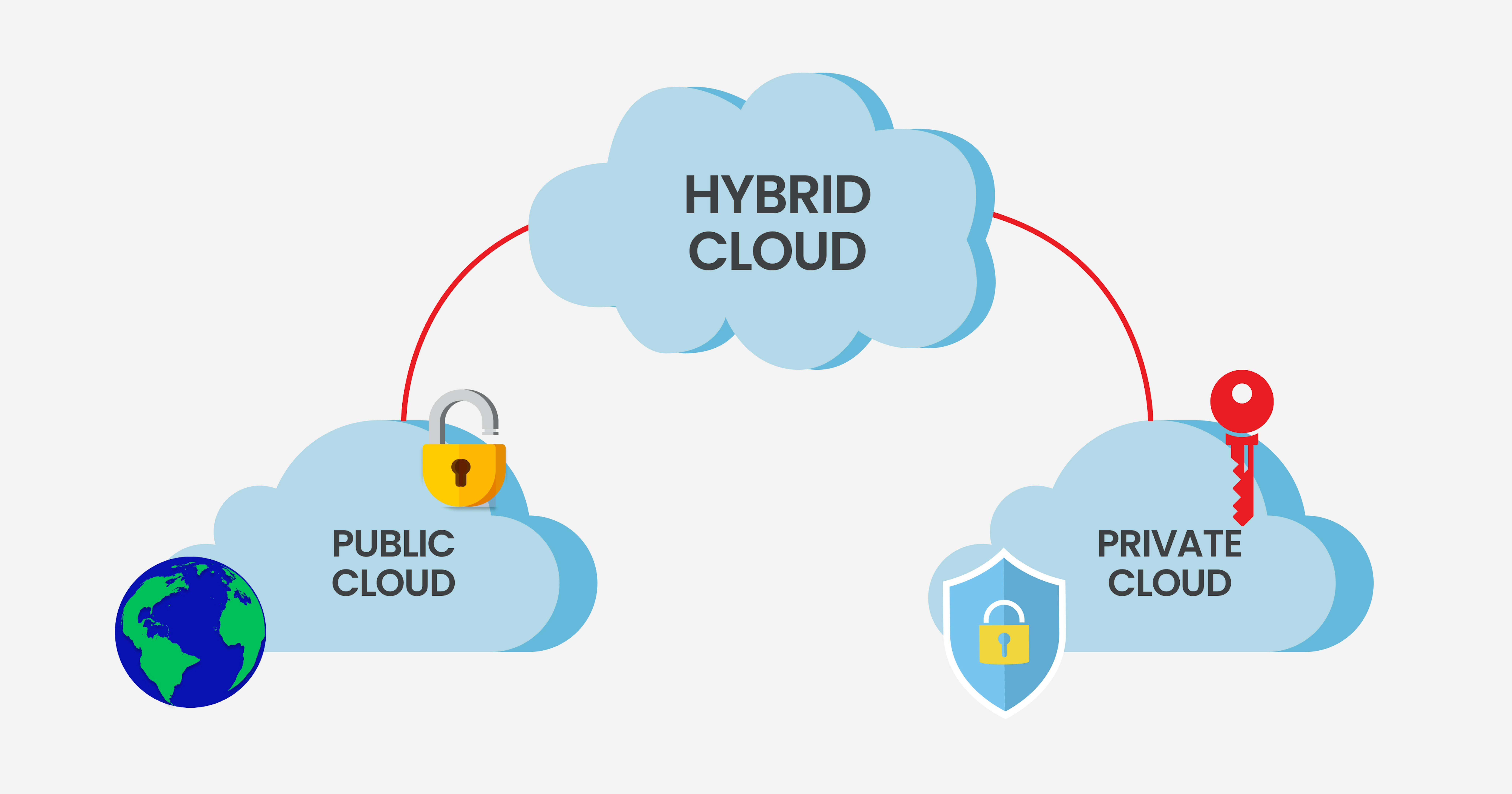
Hybrid сloud
Hybrid clouds combine the benefits of public and private clouds to provide companies with a seamless transition of workloads between the two environments based on specific requirements. For example, the public cloud can be used to store sensitive data, while the private cloud can be used to store user functions.
➕ Advantages
- Flexibility and agility: Organizations can leverage the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public clouds while maintaining control over sensitive data and applications in a private cloud.
- Improved disaster recovery: Hybrid clouds can be used for disaster recovery and business continuity, such as maintaining secondary copies of data on a public cloud in case of an on-premises outage.
- Optimized resource utilization: Organizations can optimize resource utilization by leveraging the strengths of both public and private cloud environments.
➖ Disadvantages
- Complexity: Managing a hybrid cloud environment can be complex and requires careful planning and orchestration.
- Interoperability challenges: Ensuring seamless interoperability between public and private cloud environments can be difficult.
- Higher management overhead: Managing a hybrid cloud environment requires specialized skills and expertise.
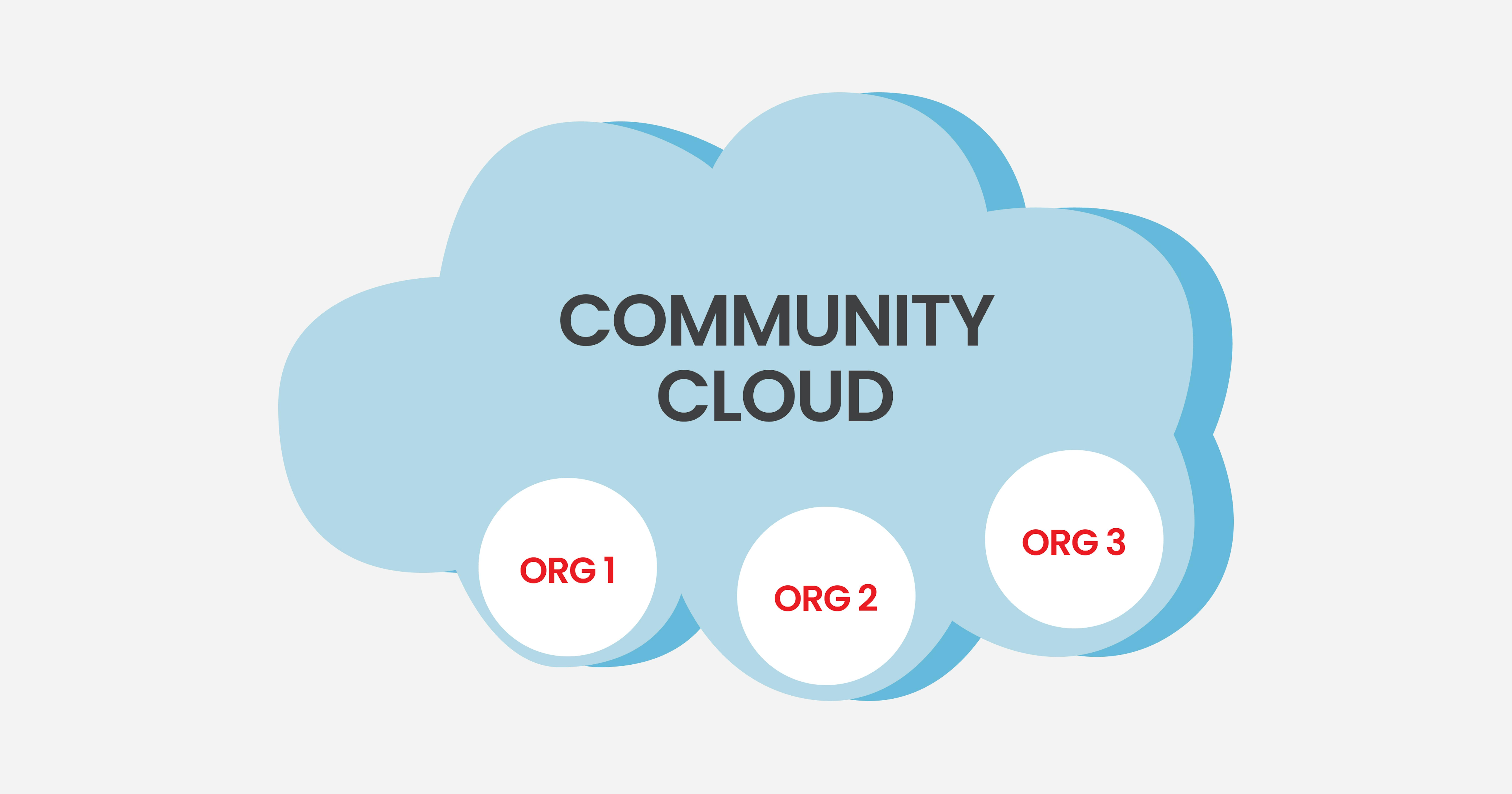
Community сloud
Community clouds support organizations that share a common cloud environment, such as government agencies, research institutions, or industry consortia. One example is universities that share computing resources with the police force. Access to a community cloud environment is typically restricted to unauthorized members.
➕ Advantages
- Cost-effectiveness: Shared infrastructure and resources can lead to significant cost savings compared to private cloud deployments.
- Enhanced collaboration: Community clouds facilitate collaboration and data sharing among organizations with common interests.
- Improved resource utilization: Shared resources can be more efficiently utilized, maximizing resource utilization and minimizing waste.
➖ Disadvantages
- Limited control: Organizations may have limited control over the infrastructure and may be subject to the policies and procedures of the community.
- Security concerns: Data security and privacy can be a concern, as data is shared with other members of the community.
- Limited flexibility: The flexibility and customization options may be limited by the requirements and needs of the community.
4 types of cloud service models
Cloud computing offers a variety of service delivery models that cater to different needs and preferences. There are three traditional models: Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS). A fourth model, Anything as a Service (XaaS), refers to the other service models delivered over the Internet on a pay-as-you-go or subscription basis.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users access the applications through a web browser or dedicated client without local installation and maintenance.
➕ Advantages
- Ease of use and accessibility: User-friendly interfaces and remote access make SaaS applications easy to use and accessible from anywhere.
- Reduced IT overhead: The cloud provider handles software updates, maintenance, and security to reduce the IT burden for organizations.
- Cost-effectiveness: Subscription-based pricing eliminates upfront costs and provides predictable budgeting.
➖ Disadvantages
- Limited customization: SaaS applications may have limited customization options, which could restrict integration with existing systems.
- Vendor lock-in: Migrating to a different SaaS provider can be complex and time-consuming due to data integration and customization challenges.
- Data security and privacy concerns: Relying on a third-party provider for data storage and processing raises concerns about data security and privacy.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides fundamental computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and networking, to users. This model allows maximum control and flexibility, as users can customize and configure the environment to their specific requirements.
➕ Advantages
- Cost-effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go pricing and on-demand provisioning reduce upfront costs and optimize resource utilization.
- Scalability and flexibility: Easily scale resources up or down to meet fluctuating demands, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
- High availability and reliability: Redundant infrastructure and disaster recovery options minimize downtime and ensure business continuity.
➖ Disadvantages
- Complexity: Managing and maintaining the infrastructure can be complex and time-consuming, requiring specialized expertise.
- Security concerns: Users are responsible for securing their own virtual machines and data, which can be a challenge.
- Vendor lock-in: Migrating to a different IaaS provider can be complex and costly and potentially hinder flexibility.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a cloud-based environment for developing, testing, and deploying applications. It includes tools and services such as operating systems, programming language execution environments, databases, and middleware.
➕ Advantages
- Simplified development and deployment: Streamlined processes and pre-configured environments accelerate development and deployment cycles.
- Reduced management overhead: The cloud provider handles infrastructure management, freeing up developers to focus on application development.
- Increased productivity and innovation: Access to a wide range of tools and services fosters innovation and experimentation.
➖ Disadvantages
- Limited customization: PaaS environments may have limitations on customization and configuration, potentially restricting flexibility.
- Vendor lock-in: Migrating to a different PaaS provider can be challenging due to platform-specific dependencies.
- Potential for higher costs: Pay-as-you-go pricing can lead to higher costs if not managed carefully, especially for resource-intensive applications.
Anything as a Service (XaaS)
XaaS extends beyond software services and offers businesses the opportunity to move away from a traditional pricing model. Instead of a flat fee for many services, the XaaS approach allows customers to pay for only the features they want to use for as long as they want. In that sense, XaaS examples include those in Saas, Paas, and IaaS, but which are provided on an as needed basis.
➕ Advantages
- Flexibility and agility: Organizations can access a wide range of services on demand to help them adapt to changing business needs quickly.
- Cost-effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go pricing and on-demand provisioning optimize resource utilization and reduce costs.
- Innovation: XaaS fosters innovation by providing access to cutting-edge technologies and services without committing to significant, long-term financial investments.
➖ Disadvantages
- Vendor lock-in: Dependence on a single provider can lead to challenges in migrating to alternative solutions.
- Security concerns: Data security and privacy can be a concern, especially with the increasing reliance on third-party providers.
- Complexity: Managing a diverse range of XaaS services can be complex and require specialized expertise.
An understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of each cloud delivery model will help organizations leverage them to build and use scalable, cost-effective, and innovative cloud-based solutions that best suit their specific needs and objectives.
Advice for choosing a cloud delivery and service model
The specific needs of every business are unique to the context and strategic plans of a company; however, there is an overall proper approach that leaders can apply to ensure the choice they make provides the expected benefits. To begin with, it involves asking the right questions during the decision-making process:
- What is the purpose of developing or implementing one of the models?
- What are the company's budget and available resources?
- How does the model fit the business continuity plan?
- Does the company's personnel have the required skillset?
For example, start-ups typically don't have the resources to invest in their own private cloud due to the costs involved and will need to rely on third-party services or a hybrid approach. Every business will need to review its resources to determine what options are available. This article has explored the advantages and disadvantages for each, and every company will need to weigh these against their current context.