Two factors determine the final price of a software development project: time and resources. Yet, companies and software developers encounter an enormous challenge in accurately estimating them. One common cause of these difficulties is a lack of communication between outsourcers and clients. Since every project is unique and requires individual components to bring it into existence, an effective exchange of information between outsourcers and clients is essential.
In this part of its series on various topics related to the software development process, Customer University, Mad Devs' experts share the details of effective project estimation. Based on their extensive experience, the team has developed a 5-stage process that incorporates communication and exchange throughout the entire process.
Stage 1. Receiving the request
Mad Devs believes in building long-term relationships with clients, which requires a thorough understanding of each client's project requirements. It also means an honest assessment of our ability to perform the necessary work. Our managers check the available expertise within the company, the project scope, and whether Mad Devs has the necessary resources to fulfilling project commitments. If the knowledge and skills correspond to the initial requirements, Mad Devs proceeds to evaluate the customer's product vision.
We have various customers who come to us for software development. Some of them are prepared with a clear vision and plan for their product, while others need assistance in forming the details. In both cases, our teams want to gain as much knowledge about the product as possible to deliver the most accurate estimates and service.
Without precise product specifications and requirements, engineers may find themselves trapped in a cycle of re-development, which in turn delays the project's completion and extends its budget. Mad Devs wants to avoid a situation like this, and customers can use the following questions to better understand their expectations for a project. Even a small answer is better than nothing, and Mad Devs is ready to help clients work out the details of any ideas that lack clarity.
7 questions to answer about a product before development
What problems does the product/solution help solve?
This question helps highlight the specific pain points a client wants to address with their solution, which helps our developers create relevant features. For example, if a product aims to streamline inventory management for small businesses, our developers want to identify pain points such as manual counting, stock discrepancies, and reordering delays to build appropriate automation and notification systems.What is the desired result?
Clear expected outcomes ensure that development efforts align with the client's business objectives. This question gives us measurable success criteria and helps us avoid scope creep during the development process. Clutch.co, the successful B2B review platform, approached Mad Devs with the aim of improving its website’s performance, and our developers prioritized features that contributed to this goal.How will this system interact with other systems?
This question emphasises the technical requirements, potential compatibility issues, and integration points that might affect development complexity and timeline. So if the client wants to implement a new CRM system to exchange customer data with their existing accounting software, our developers must consider the API requirements, data transformation needs, and security protocols between these systems.Are any integrations required?
Specifying necessary integrations upfront helps us prevent costly rework and ensures compatibility with other technologies. For example, third-party services, APIs, or platforms that a solution must connect with to deliver its full value. When Mad Devs worked on a project with GoDee to develop software for their shuttle buses, the client requested integrations with payment options, GPS tracking, and other features. This information provided our developers with the necessary information to plan suitable connection points and data flows.Who are the users?
Our team needs information about users that could influence the product's design. For instance, if the primary users are elderly individuals with limited technology experience, developers would prioritize larger text, simplified navigation, and clear instructions over complex features that might confuse this demographic.What are the main UI/UX design requirements?
When clients express clear interface and experience expectations, developers can establish visual identity requirements, accessibility standards, and interaction patterns that should be consistent throughout the app. For instance, the Bilim, an app that educates women and girls on important health topics, required a simple and efficient design. Mad Devs' developers focused on minimalist interfaces with calls to action and streamlined user journeys rather than feature-rich screens that could overwhelm the app’s users.What are the key benefits and competitive advantages of the product?
Understanding a product's unique value proposition helps our developers emphasize and enhance it in the software design. For example, if a product's main advantage is its ability to process data faster than competitors, our teams would prioritize performance optimization, efficient algorithms, and real-time processing capabilities to strengthen this key selling point.
Again, answers to these questions are nice to have, but our experts are available to help clients understand their aims and products when they lack an understanding of these details.
Stage 2: Understanding the factors that affect development
The next step involves four sub-stages and the following questions:
- Research: Do any similar solutions exist?
- Scope estimation: What are all the steps involved in the project?
- Velocity: What is the timeframe for the scope?
- Risks and uncertainty: What percentage of risk is suitable for this project?
Research
Our managers study the functionality that serves the customer's needs most effectively and search for any third-party solutions that we can use to deliver the expected results. Today, not all the elements of a software project need to be developed from scratch. Mad Devs prefers saving time and reducing development costs by using a ready-made solution without coding, if it works for a given product.
Scope estimation
The next step is to estimate the project's scope in terms of the effort and time required. This is helpful for determining the cost of fixed-price contracts and useful when discussing a customer's needs. There are several important elements to identify in this process:
- Scope: Identify the scope of the project based on the provided requirements.
- Decomposition: Break the project into logical 'mini' releases that contribute to the whole product.
- Sizing: Determine the size of the team required to complete the project and the seniority level of the developers.
- Review: Colleagues review the plan to confirm the estimation is correct.
- Finalization: We aggregate all the estimations from components and functions and have a baseline estimate.
Velocity
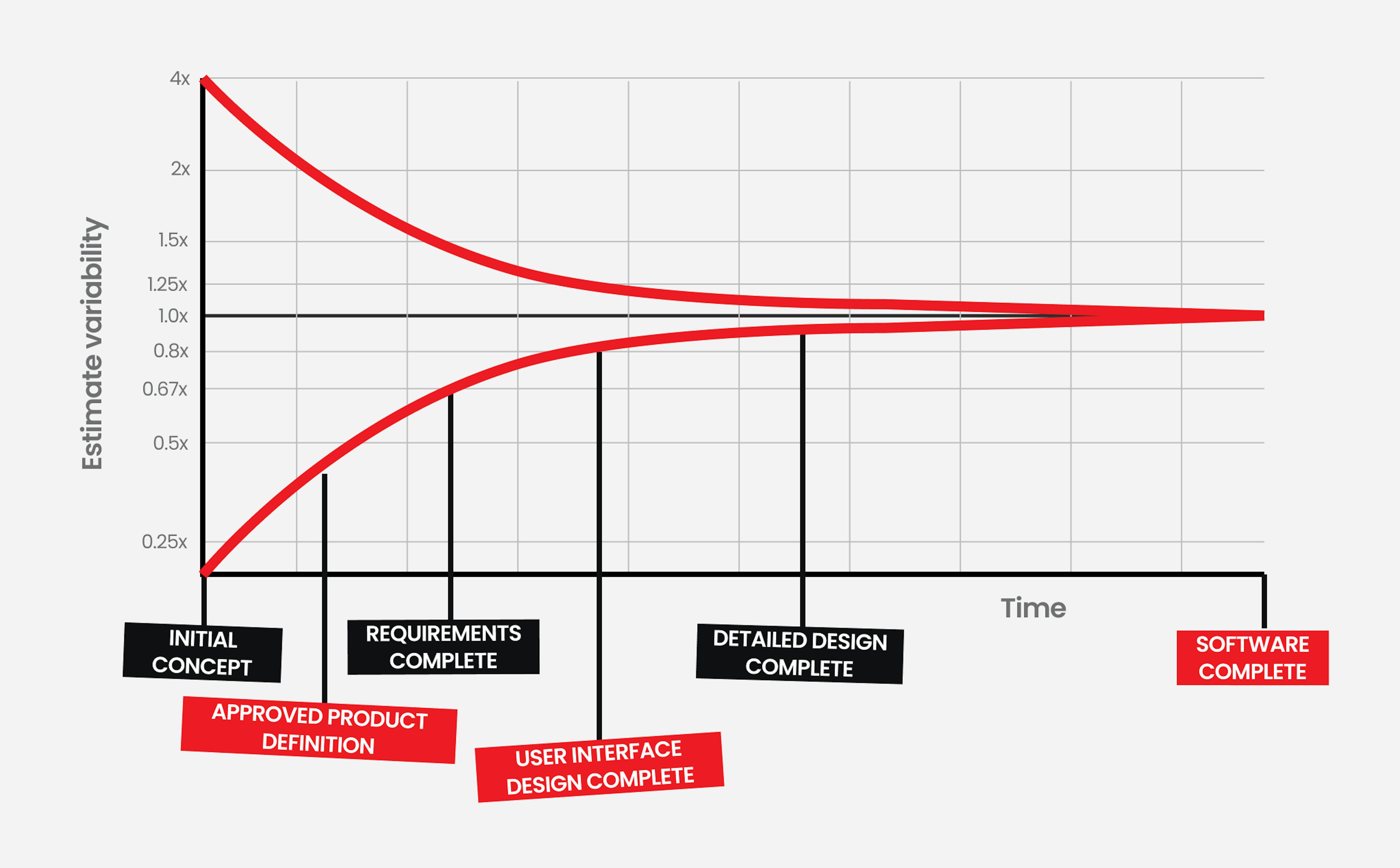
Velocity refers to a team's capacity to complete work within a given iteration (or sprint) and expresses this range, typically based on the start of a project. With a clear scope and path, the team adds up the effort estimates associated with the completed user stories during each iteration to understand the velocity, which managers use to plan releases and adapt workflows and processes as the project progresses. Regular review of velocity enables the Mad Devs team to adjust its forecast and limits the amount of work taken on in subsequent iterations.
Risks and uncertainty
All software projects come with a certain level of uncertainty, which decreases as development progresses and the client approves features. Mad Devs includes a 15-20% risk "cushion" in project estimations to account for unforeseen situations. For example, if a project suddenly requires specific expertise or more experienced engineers to deliver a function, this cushion provides the desired level of flexibility to make necessary adjustments in work scope. The percentage Mad Devs uses is based on extensive experience with various projects, and our teams understand how to mitigate risks if they occur.
This also involves a "development tax" that refers to technical debt, quality assurance tests, and keeping up-to-date documentation. These additional processes are necessary investments to ensure a product's stability and scalability.
Stage 3: Choosing the cooperation model
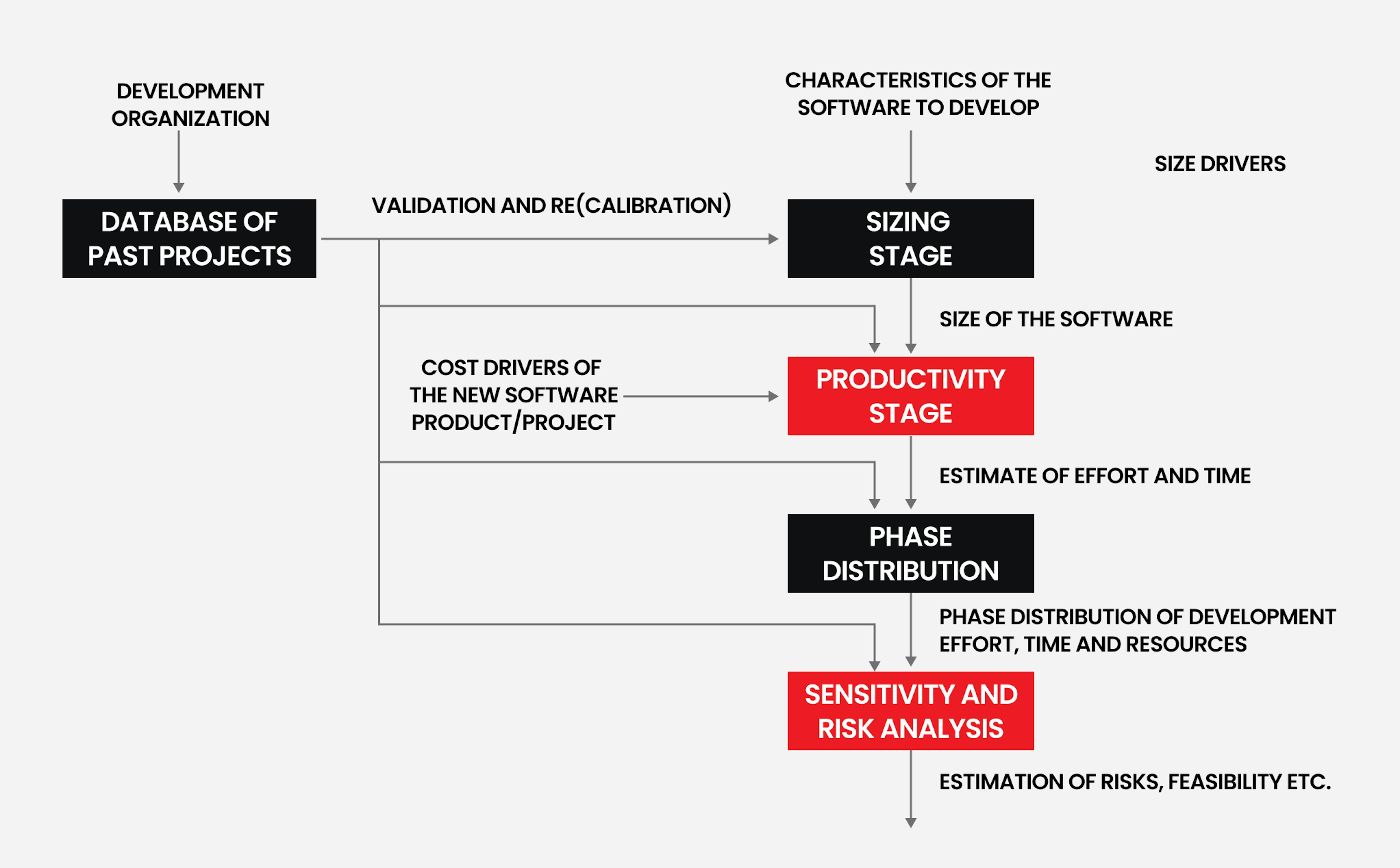
The steps above help create an accurate picture of the project and the work that needs to be done. The next part of the process involves selecting the right cooperation model that best suits the client and their project. Mad Devs uses various models that account for a customer's preferences. For some, the right model may be clear, while others may require an understanding of the available options. Below, please find a description of each cooperation model:
- Staff augmentation: Individual specialists from Mad Devs are assigned to a client's team to complete tasks.
- Project-based dedicated team: An entire team (which typically includes a project manager) is provided to the client to undertake the project from start to finish.
- Temp to hire: Similar to staff augmentation, but clients look to hire temporary specialists as full-time employees.
- Technical assessment & consulting: Mad Devs' technical experts perform analysis for the client and provide recommendations.
- Team supervision: Managers and team leads from Mad Devs supervise the client's current team and help manage it more effectively.
- Legacy software management & project transfer: Mad Devs takes on projects that other teams have worked on but failed to deliver desirable results.
While each model is unique in what it delivers to a client, the basic elements of the calculation are the same: team size and time.
Stage 4: Calculating the cost
Mad Devs' 3 best practices for successful software cost estimation
Even with the Mad Devs' plan, estimating the cost of a software development project can be difficult. Here are the 3 best practices Mad Devs uses to ensure accurate forecasts and price estimations that deliver better customer experiences and build trust for long-term relationships.
- Use data: Businesses can use AI-powered data collection, such as Enji, to gather data from previous projects for accurate estimations based on similar features.
- Build in a learning curve: Include the time required for developers to learn new tools or topics into timeline predictions.
- Embrace AI tools: The modern software engineer is more than a coder. AI tools can reduce the time spent on a project and free engineers' time for creative approaches.
Once all the information mentioned above is clear, there are different ways to calculate the cost for a software development project.
Traditional approach
This approach fixes the project's scope and keeps time and budget as variables that can change. In this case, the logic is straightforward, but if the time spent on the project becomes flexible, there is a risk that important deadlines may be missed or the timeframe may extend beyond any reasonable return on investment. Likewise, a flexible approach to cost may result in unexpected changes that increase the amount on a client's invoice.
This approach is too rigid to account for changes that can occur in a project's scope as development progresses; for example, when market and user research identify a feature that needs to be added or removed.
Agile approach
Unlike the traditional approach, this means of estimating project cost fixes the time and cost to allow the scope flexibility to account for expected adjustments. In this scenario, the project's scope is broken down into results that can be delivered as separate packages. Clients pay for each package and can decide to stop development once they receive everything for a viable product.
The agile approach increases transparency within the estimation process and provides room for adding new features if the client decides they are needed. Likewise, when a project is divided into packages, it's easier to estimate the cost of additions to the project's scope based on data and experience.
Algorithmic cost modeling
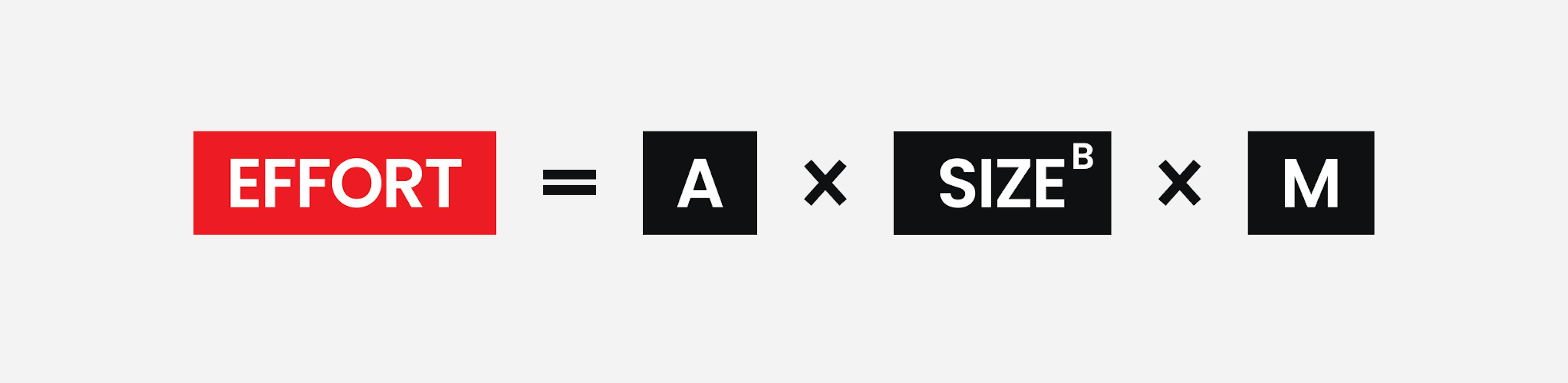
This approach to cost modeling uses a mathematical formula to predict project costs based on estimates of the project's size, the number of software engineers involved, and other process and product factors. In its most general form, this model can be expressed as:
Stage 3. Choosing the cooperation model
Over the last years, Mad Devs gained experience in 50+ large-scale projects. In the light of the knowledge gained, we developed 360-degree expertise and suggested solutions that fit customers' business needs.
Outsourcing and outstaffing are traditionally two of the most common cooperation models. Let’s elaborate on them before addressing the more advanced and modernized classification. In some instances, we incorporate a hybrid cooperation model.
- A: A constant factor that depends on local organizational practices and the software type being developed.
- Size: Either an assessment of the software’s code size or a functionality estimate expressed in function or object points.
- B: Refers to the challenge of the task, and its value is between 1 and 1.5.
- M: A multiplier made by combining process, product, and development attributes, such as the requirements for the software and the development team's experience.
As a software's size increases, additional costs appear that are associated with the communication overhead of larger teams and other factors. This ties in with common difficulties of all algorithmic models:
- Estimating the Size is a challenge at an early stage in a project. It's easier to estimate the size of functions and objects than code size, but they are often still inaccurate.
- The estimates of the factors contributing to B and M are subjective and can differ depending on an engineer’s background and experience with the system.
Despite challenges in the early stage of a project, companies use cost estimation algorithms and create a range of estimates (worst, expected, and best) that they can apply to their calculations. As the software process continues, more information becomes available to make the estimates more accurate.
Mad Devs' strategy
Mad Devs uses the Time & Material model to provide greater flexibility. In this arrangement, clients pay for the time our teams spend on their projects, and Mad Devs applies time tracking to both internal and external projects. With the Time & Material model, a project enjoys a stable monthly budget, while the scope and tasks can be reconsidered. The alternative—the fixed price model—is rigid, and any changes in the initial plans require revising the contract. In some cases, clients prefer the second approach, and our teams are happy to work with them. Click here to learn more about the differences in pricing models.
The basic formula is:

The first essential element in the formula above is time. We include estimates of the whole product development process, including dealing with technical debt and real users' feedback when calculating it.
The second element is the team. The team can consist of developers with different seniority levels (Junior, Middle, and Senior), which affects the rates. Our managers work to match our developers' expertise with a project to find the best balance that ensures both high quality and a reasonable price. Then, we explain the reasons for a team's composition in the proposal.
Stage 5: Proposal agreement and negotiation
The proposal that a client receives reflects all the information gathered in the previous steps. Still, it's essential to dedicate time to crafting the proposal and negotiating the details. The client needs to review the proposal and determine if it matches their short and long-term vision for the product. They should also see a clear estimation of the project's cost and duration. At Mad Devs, managers present the plan, after which the client can adjust it as needed. This may require multiple interactions and re-estimation, but the aim is to find a result that satisfies both parties.
A Mad Devs proposal breaks down the prices and includes the following sections:
- Project goals
- Project brief
- Detailed information on tasks
- Team composition
- High-level project roadmap
- Development plan and duration
- Cost procedure and quotation assumptions
Trusted IT partner
Mad Devs applies these approaches and techniques to build trust between team members and allow customers to see how much time and resources it will take to build a product. Mad Devs is focused on delivering value through software development that addresses end-users' wants and needs, which is one of the reasons why customers choose Mad Devs over other software development companies. Others include:
- Expertise in long-term, stable, scalable, and complex products.
- Transparency in organizational and development processes.
- Value-oriented development.
- Commitment and determination to achieve project results.
Proposals outline the optimal approach for a project, including the required time and resources. Then, Mad Devs gives clients visibility into our plans, processes, and calculations from start to finish during a project.
If you have questions or want to discover more details, get in touch with us.