Analyze with AI
Get AI-powered insights from this Mad Devs article:
Developing a mobile application from A to Z is rather long and laborious work. But we have prepared for you a practical application development process in six main stages. It will help you in creating your project, regardless of the scale. Buckle up, we start.
Why invest in mobile app development
According to data.ai report, mobile app spending hit a record-breaking $533 billion in 2023, making the app economy a half-trillion dollar industry. This translates to nearly $1.5 billion spent daily on mobile apps and advertising. In fact, mobile ad spending reached $362 billion, reflecting an impressive 8% increase year-over-year.
Mobile apps have become a game-changer for businesses, driving not only customer engagement but also innovation and new revenue streams. Here's a breakdown of the key reasons businesses are investing in mobile app development:
1. Deeper customer connections and loyalty
Mobile apps provide a direct channel to connect with customers. Businesses can personalize the experience, offer targeted promotions, and provide easier access to products – all factors that foster stronger customer relationships and loyalty. This translates to a better return on investment (ROI) for your mobile app efforts.
2. Empowering your workforce
Mobile apps can equip employees with the tools they need to succeed, regardless of location. With real-time access to work information and customer data, employees can be more productive and efficient. Mobile apps can also automate repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-level work. This translates to increased employee satisfaction and retention, especially in today's hybrid and remote work environments.
3. Fostering a culture of innovation
Mobile apps are no longer just for shopping or social media. They offer features like data security, personalization, image recognition, messaging, games, sharing, and payments. With tools like cloud computing, AR, and AI, businesses can add even more to their apps, making the development process more intricate. Companies that embrace this culture of innovation can position themselves as leaders in their field.
4. Unlocking new revenue streams
Mobile apps can streamline existing business processes and open doors to new revenue opportunities. By digitizing operations, companies can create new products and services for existing customers and reach entirely new audiences. This allows businesses to expand their reach and unlock significant growth potential.
In total, the mere presence of a mobile application does not solve all business problems, but in the right hands, it becomes a powerful tool for increasing profits.
Creating a mobile app for your business can be a game-changer, but it's not always easy to know where to start. With a proven app development process, success can be within reach. Our seven-step mobile development process can help you navigate. Let's elaborate.
7 steps of mobile application development
Here you can find six main stages of mobile app development and team members who are involved in each of its steps.

1. Strategy
The first and most important step is a strategy to turn your idea into a working application. The strategy determines the value of your application, significantly affects the functionality and interaction with the audience.
To develop a strategy, you need to answer the following questions:
- Who are the users of your mobile application?
- Who are your competitors and what are they doing?
- What are the goals and objectives of your application?
- What is the preferred mobile platform for the app?
Team members: project manager / product manager, designer, iOS developer / Android developer
2. Analysis and planning
After you have outlined the strategy, you can proceed to prepare the implementation of the project. It all starts with defining the use cases for the application and identifying the functional requirements. Why is it important? Mobile apps for IOS and Android use different technology stacks. This means that you need developers with specific skills or a team that brings together iOS developers and Android developers. This will help you with a roadmap detailing the development stages with time frames for implementation. In other words, this is analysis and planning.
Team members: project manager / product manager, designer, iOS developer / Android developer, backend developer, quality assurance engineer
3. Design
Information architecture & workflows
At this stage, you need to prepare the data. They can be divided into two categories:
- Data that users see directly in the application—information about the company, services, catalog, bonus offers, etc.
- Data that the application will collect about users for you—contact information, how users interact with the application (links, responses, reviews)
It is recommended that you develop an information architecture for your application. This will help you visually see the user journey ahead of time.
UI/UX
Then you can move on to choosing an application design. And this is the most creative stage. Keep in mind, however, that the point of the design is not only beauty and creativity but also so that users can easily and easily use your application. This is the meaning of the UI/UX design of a mobile application. You have to keep in mind that a good mobile application should have a clear and convenient user interface that grabs and retains attention. If the person is making the extra effort to find contact information, register, etc., then think twice about what you came up with.
Wireframes
Wireframes are used to keep UI/UX design in mind. It's like sketches of drawings for an application, but only digitally. Conceptual layouts that create a visual structure with application functionality. This is where aesthetics and convenience meet. But don't focus on colors, fonts, and styles. Since at this stage, more of the frame is taken into account, which rests on the design of the device. iPhone, Ipad, Android devices have different resolutions. It is important that the application is responsive to the specific device interface and user experience.
Style guide
When the wireframes are ready, you can jump directly to the style guide. This is a kind of directory where all the application design standards are collected. It includes company branding, color scheme, icons, button designs.
In addition to the visual component, the style guide also influences the mobile app promotion strategy. It contributes to the recognition of the mobile application in the market.
To create a good style guide, you need to consider:
- What fonts will be used for the texts?
- What is the preferred color scheme?
- How to link your brand and mobile app design?
Mockups

All that was above was preparation for creating mockups. Based on the style guide and wireframes, a visualization of the mobile application, layouts, is created. It can be either a mockup of a 3D model or a PSD file with a photo. The purpose of the mockups is the same: to superimpose your design on the template. But this, of course, does not mean that changes and improvements will not be made during the development process.
Prototype
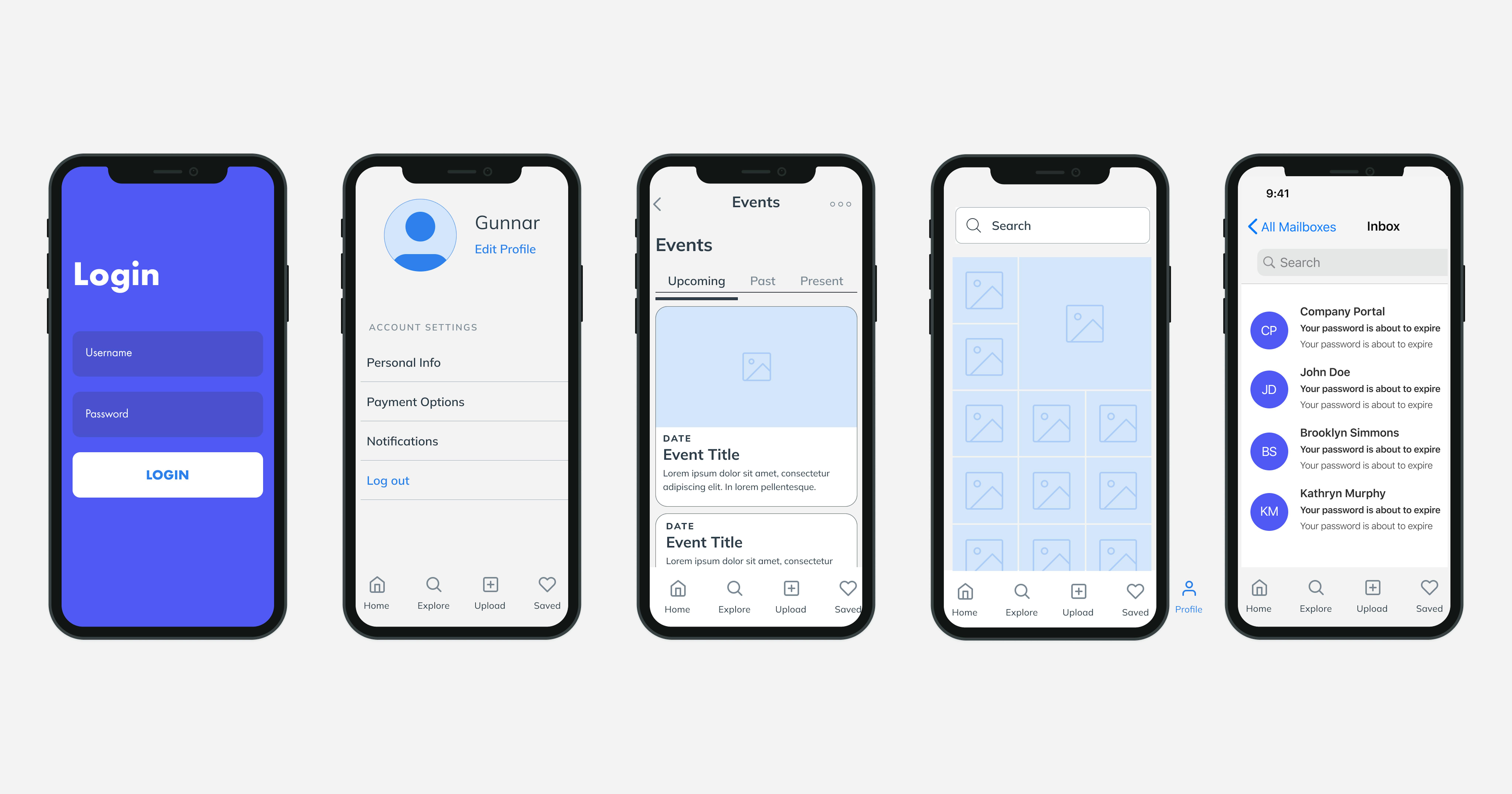
We talked about possible changes to mockups above. Prototypes help with this. If mockups display static design, then prototypes are a test, but not yet the final model of the future product, which can already be seen in this work, touched and evaluated. This is actually a ready-made sample not just a drawing on paper. An application interface prototype helps to represent the design and logic of the application, as well as to test the idea of the application. It is stuffed with replicas and is tailored to work only in certain situations and with a certain set of data, but this is already enough to collect a response from the target audience.
Team members: project manager / product manager, designer, iOS developer / Android developer, copywriter
4. App development
In fact, if you "dissect" a mobile application, you can divide it into two main components:
- Mobile app front-end is the "face" of app. What you see in the application.
- Back-end/server technology is the "shadow" part. What makes the application work.
For example, you pay for a purchase in the app: enter the card details, click "pay" and you see the inscription "your payment has been accepted for processing"—it was a frontend. How your money moves within the network and how your order enters the store is a backend. Accordingly, when the store sees a notification that an order has been received, and the money has been credited to the account, this is again the work of the frontend.
Let's take a closer look at each component.
The backend
The backend is the engine that powers your app. Here, your development team focuses on:
- Databases and server-side objects: These store your app's data and manage functionality behind the scenes, impacting performance.
- Coding languages: Choosing the right languages (Java, Python, etc.) is crucial for building a robust backend.
- Database engine and hosting: Selecting the right database engine and hosting environment ensures smooth operation and scalability.
The frontend
The frontend is what users interact with directly. Here's a breakdown of common approaches to building it:
- Native apps (platform-specific): These apps are built specifically for iOS or Android, offering optimal speed and responsiveness. While potentially more expensive due to separate codebases for each platform, the user experience can be unmatched.
- Cross-platform apps: This approach allows you to build an app with a single codebase that runs on both iOS and Android. This saves development time and cost, but may have slight performance limitations compared to native apps.
- Hybrid apps: Combining elements of native and web apps, hybrid solutions use web technologies within a native app shell. This allows for a multi-platform app while being quicker to build than a pure cross-platform solution.
At this stage, we are working closely with the developers. The most necessary thing is to define a programming language, a technology stack for a mobile platform, and a database as a back end.
Team members: project manager / product manager, designer, iOS developer / Android developer, backend developer
5. Testing
Next, we move on to the testing phase. This makes your application stable, user-friendly, and secure.
The testing process looks like this:
User experience testing
The purpose of this testing is to ensure that the final product matches the intended user experience. It covers interfaces, navigation, interactivity of the application.
Functional testing
It is important to involve as many users as possible in order to test all the functions of the application. It so happens that two users fill out the same form and end up with different results. This way you can be sure that the mobile application as whole works properly (system testing), as well as its individual functions (unit testing).
Performance testing
There are many basic performance criteria but we can highlight a few of them:
- How fast are the app's screens loading?
- Does your app leverage network bandwidth efficiently?
- Is the size of your application appropriate?
- How strongly does your application affect the device's charge level?
- Does your app handle the load and perform well even when usage spikes?
Security testing
This testing is of the utmost importance. It is essential to avoid application vulnerabilities in order to avoid hacks. Especially if your users enter their credentials into the system. Login sessions (when the username and password are entered) should be monitored on the device and on the server-side.
Testing devices and platforms
The bottom line is that mobile devices and their operating systems are updated regularly. New models come out, updates for IOS and Android are released almost every season. Therefore, your mobile application needs to be tested on multiple mobile devices or device simulators. Have you noticed that new popular applications are most often released for Apple iOS, and after a while for the Android platform? It's about Apple's controlled environment as they control both the hardware and the OS. And Android platforms are famous for open source code, hence the difficulty in developing a mobile application for them.
Team members: project manager / product manager, iOS developer / Android developer, backend developer, quality assurance engineer
6. Deployment

And the most ceremonial part of the launch is the submission of the application to the app stores. All that remains is to create a developer account in the Apple App Store and Google Play Store.
A little metadata reference for releasing an app for submitting:
- App name
- Description
- Category
- Keywords
- Launch icon
- Application screenshots
Then it remains to wait. In the App Store, you will need to wait until the Apple iOS Guidelines are verified. And Android does not have a verification process, applications become available in the Google Play store within a few hours after submission.
Team members: project manager / product manager, iOS developer / Android developer, backend developer
Team to choose
To create a mobile application, you must assemble a team of specialists. Their number depends on the amount of work and the complexity of the idea of the functionality. But the basic set looks like this:
- Project manager / product manager
- Designer
- Copywriter
- iOS developer / Android developer
- Backend developer
- Quality assurance engineer
To choose the appropriate team size for your app development project, you should make an initial estimate of your project development scope. To do this, you need to consider the following factors:
- Choice of platforms to launch your app on
- Complexity of your app and the scope of work
- Team members expertise
- Terms of app development
- Budget
Another important point is where to find a mobile app development team. You have five ways to employ specialists to develop your app:
Model 1 — In-house developers are specialists sitting in your office and working full-time only on your project. It allows you to control the development process and choose team members on your own.
Model 2 — Freelancers are useful when you need one-time tasks and high-level specialists. You can choose freelancers by browsing their portfolios on freelance platforms.
Model 3 — A dedicated team is a group of remote IT specialists from a third-party service provider. The benefit is that you can hire a complete pack of specialists (designers, developers, QA engineers, product and project managers) at one time. They can fully work on your project or collaborate with your in-house team members while remaining employees of the third-party service provider.
Model 4 — Outstaffing is a model that refers to hiring additional employees for a project. It is an effective way to improve the efficiency of your development team for the app implementation period.
Model 5 — Outsourcing means that you hire a company for the entire app implementation from start to finish. It takes care of the tools and resources necessary for successful execution and takes responsibility for the final result and risks.
Model 6 — Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) that allows you to hire remote experts with an option to transfer full-time for your company. The main advantage of this model is recruiting, onboarding, and HR assistance is on service company, Mad Devs, for example.
To wrap up
A well-designed app can boost revenue and strengthen your connection with your audience. Mobile app development is a long and interesting process that might seem daunting, but with the right guidance and tools, it's more accessible than you think.
At Mad Devs, we've supported mobile app development for various industries, including finance, healthcare, retail, and more. If you have questions about turning your idea into a successful app or need further assistance, feel free to contact us for a free consultation on your mobile or digital projects.