The complexity of today's modern environment demands a new security model that can effectively adapt to the changes. It should also protect the data and devices of organizations while enabling them to work seamlessly in the hybrid workplace. Therefore, zero trust security is becoming an increasingly popular way to protect data.
In this article, let's break down the zero trust strategy, what the benefits are, and how to integrate it into your company.
What is zero trust?
A zero-trust strategy is a cybersecurity approach that focuses on the context that is established through the use of strict user authentication and access controls. It can help organizations improve their cyber threat defense and simplify their network infrastructure.
Zero trust architecture components focus on the implementation of strict access controls and eliminating pre-authorized user access.
Understanding the need for zero trust architecture
Due to the evolution of networking and the rise of cloud computing, the complexity of enterprise architecture has increased, creating multiple security layers that can be difficult to enforce and manage. This makes it even more important that the IT and security teams can provide secure remote access to their employees.
Modern networks need a more secure approach to security due to the complexity of their entry points. Traditional perimeter-based methods can't adequately address the needs of modern enterprises due to their lack of integration and security controls.
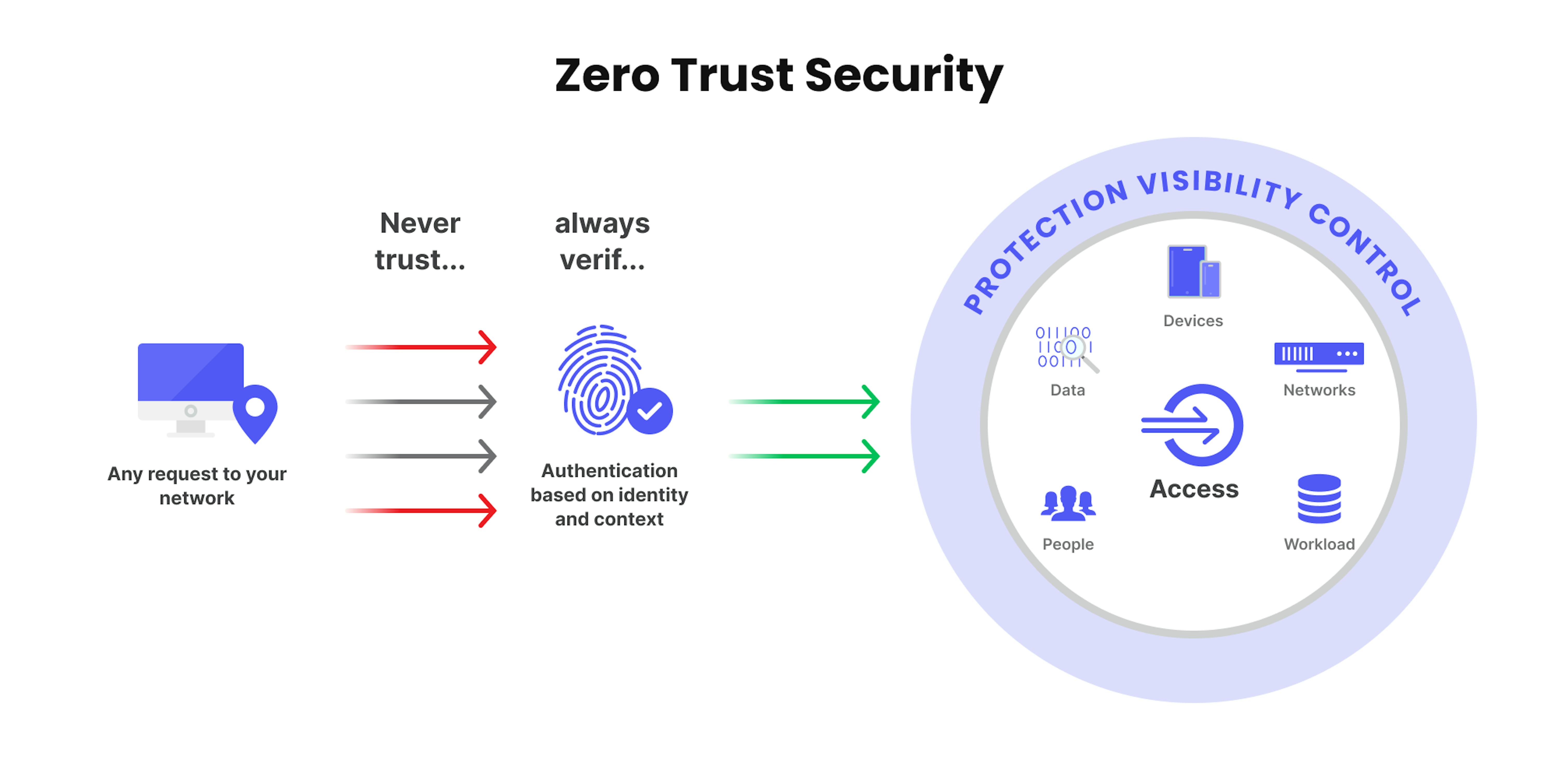
The concept of a zero-trust architecture is based on the belief that no trust is ever granted. It helps organizations protect their modern environments while enabling digital transformation. It applies a set of policies that are designed to prevent unauthorized access and movement across an organization's network. These policies can be based on the user's location, role, and device.
Zero trust strategy requires visibility into the traffic and users in the environment. It can also be done through the use of robust multi-factor authentication methods, such as those used by Apple.
How zero trust works
This framework combines the advantages of cloud workload technology, identity protection, and next-generation endpoint and security to ensure that systems are secure. It also considers the various factors that affect the system's hygiene, such as email encryption and the risk of unauthorized access.
The simple model can be illustrated with this picture:
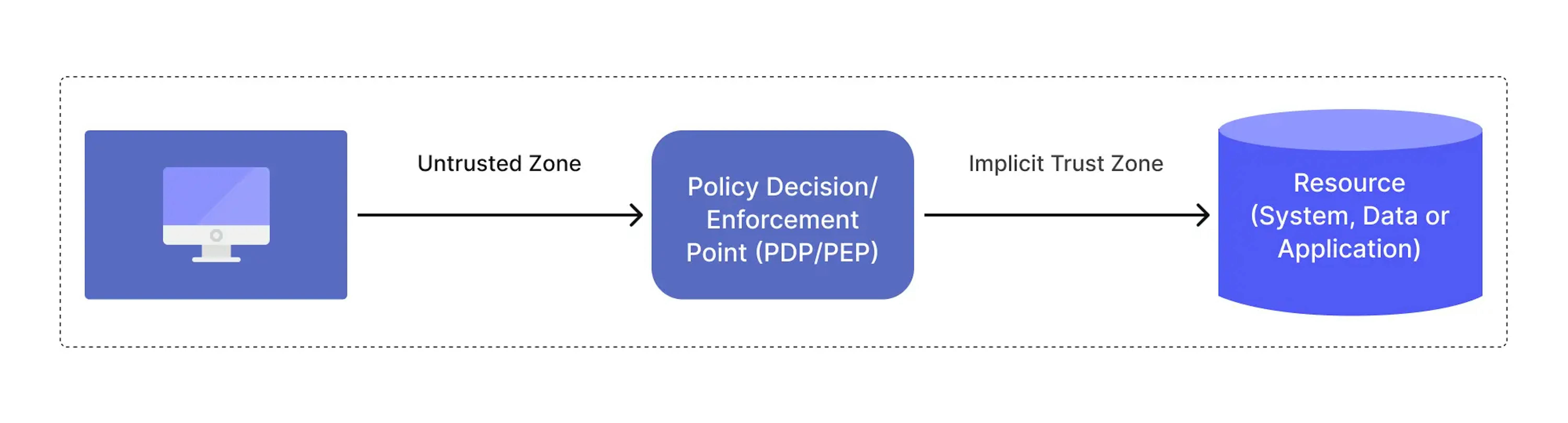
Where the implicit trust zone represents an area where all the entities are trusted to at least the level of the last PDP/PEP gateway. For example, consider the passenger screening model in an airport. All passengers pass through the airport security checkpoint (PDP/PEP) to access the boarding gates. The passengers, airport employees, aircraft crew, etc., mill about in the terminal area, and all the individuals are considered trusted. In this model, the implicit trust zone is the boarding area.
What are the principles of a zero trust model?
According to the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Zero Trust Architecture Guide, zero trust solutions must be designed according to the following principles:
- Any access to resources should be governed by company policies, which should take into account multiple factors including the user; operational attributes such as IP address and operating system; work schedules; and locations.
- Access to corporate resources or networks must be on a per-request basis and must require secure user authentication.
- Authentication of a user or device should not automatically provide access to other resources.
- All communications with or between corporate resources and networks must be encrypted and authenticated to provide secure access. Systems must apply the appropriate security level depending on the user’s context—for example, whether a request comes from within the network or a remote access point.
- All devices and data must be defined as corporate resources and secured using zero-trust principles. This includes servers, workstations, mobile devices, and any device with access to corporate networks or data.
How to implement zero trust architecture?
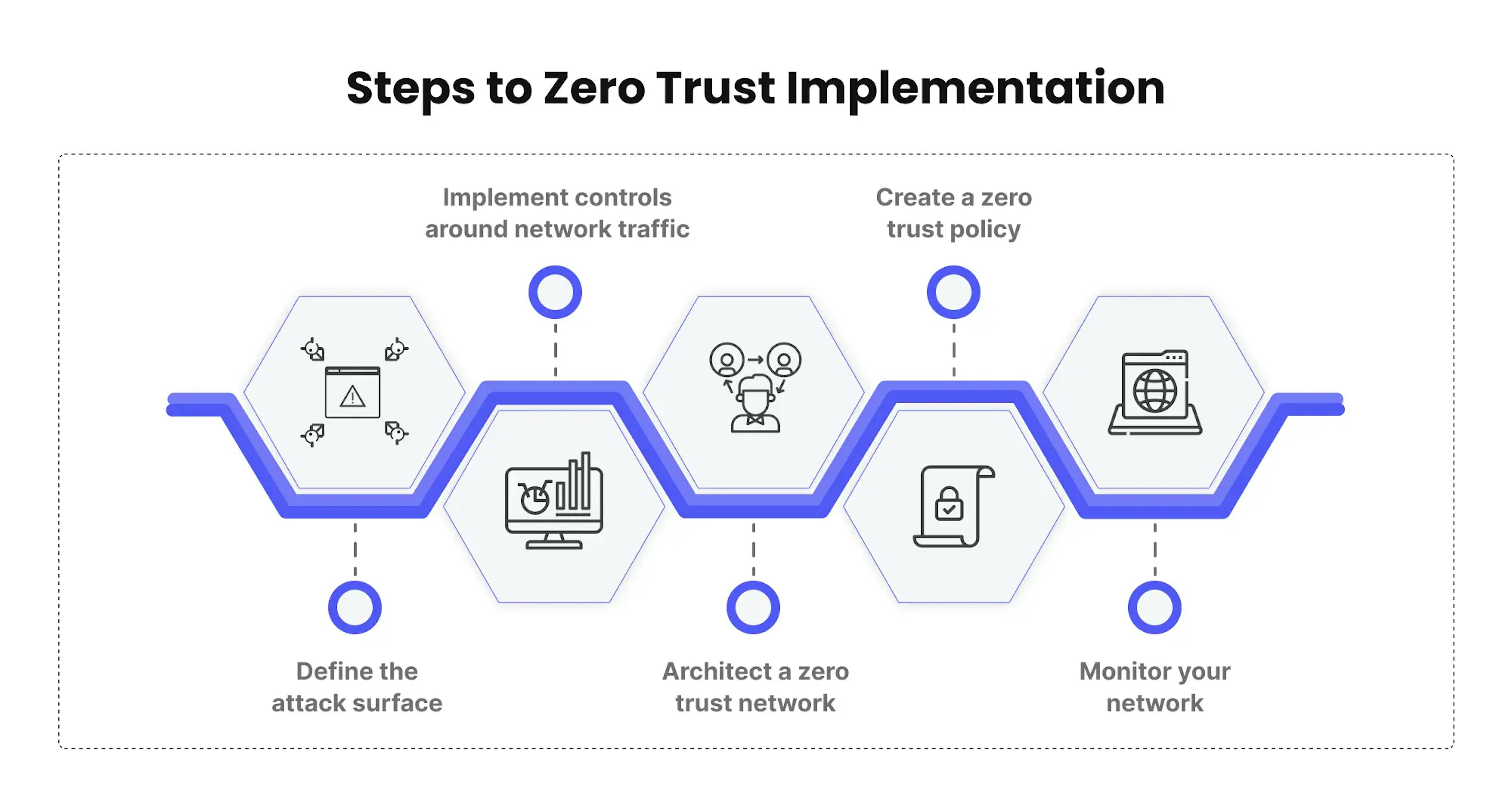
Define the attack surface
Defining your attack surface should be the first item on your zero-trust checklist. To do this, you want to hone in on the areas you need to protect. This way, you will be able to implement policies and deploy tools across your entire network. Focus on your most valuable digital assets.
- Sensitive data. The sensitive data that an organization collects and stores, such as its customers' and employees' personal information, can be easily stolen by thieves.
- Critical applications. These are the applications and data that are vital to your business operations.
- Physical assets. Physical assets such as POS terminals, IoT devices, and medical equipment can also be stolen by thieves.
- Corporate services. These include the various components of an organization's infrastructure that support the day-to-day operations of its employees and executives.
Implement controls around network traffic
The way traffic flows across your network will depend on the various dependencies that each system has. For instance, if an organization has a database that holds information about its customers, then many systems would need to access this data.
The way requests are routed through a database is very important to ensure that they are protected from unauthorized access. This is because the information in the database is delicate and sensitive. Understanding the details of the network architecture will help you determine which network controls should be implemented and where to place them.
Create a zero trust policy
After you have architected the network, you will want to design your zero-trust policies. This is most effectively done using what is known as the Kipling Method: who, what, when, where, why, and how for every user, device, and network that wants to gain access.
Architect a zero trust network
A zero-trust network is designed to protect specific areas of the network. In most cases, a next-generation firewall will be used as a tool to segment the network.
Although zero trust is often associated with securing only users, a comprehensive approach is also needed to protect the various components of an organization's infrastructure.
- Before you start implementing a zero-trust strategy, it's important that the users are secure. This includes implementing a variety of security measures such as multi-factor authentication and the use of low-access policies.
- Zero trust in applications is a concept that eliminates the implicit trust that various components of them have when interacting with one another. It requires continuous monitoring to ensure that the applications are following proper behavior.
- The various components of an organization’s infrastructure, such as switches, routers, IoT, supply chain, and the cloud, should also be protected from unauthorized access using an enterprise-wide zero-trust strategy.
Monitor your network
One of the most critical steps that you can take to ensure that your network is secure is to monitor its activity. It can help you identify potential issues and provide valuable insight into the performance of your network. Pay attention to the following:
- Reports—a regular or ongoing report can be used to flag anomalous behavior. You can then analyze the data to learn how your system or employee is affected by your zero-trust system.
- Analytics—the data collected by your system can be used to provide insight into how well it functions. This is useful when you need to monitor the behavior of your users and the performance of certain components of the network.
- Logs—the logs produced by your system can provide you with a permanent record of activity. They can be analyzed manually or with the help of analytical tools, which can identify patterns and anomalies.
Examples of zero trust practices in big companies
Google zero trust architecture

Google BeyondCorp uses the company's zero-trust security model to help organizations create secure environments. It was created as an extension of the firm's security principles introduced in 2012. The company's internal initiative behind BeyondCorp was to enable employees to work from anywhere without using a VPN. Since then, it has been used by most Google employees to provide device- and user-based authorization and authentication for the company's corporate resources.
The BeyondCorp access controls model enables organizations to grant users access to certain resources based on their roles and identities instead of where they are connected.
Instead of relying on passwords, Google's BeyondCorp uses identity as the basis for its access controls. This method ensures that every user is authenticated and identified before they can access a particular resource, which helps prevent security breaches.
Microsoft Zero trust architecture

The scope of the zero trust implementation was to provide a single sign-on for all of the company's corporate services, such as Office apps and line-of-business applications. It was implemented on the core applications that employees use daily on platforms such as iOS and Android.
Windows Hello for Business allowed us to enhance the strength of our authentication process by implementing a variety of features, such as device management and health validation. They also introduced a Windows Virtual Desktop, which allows employees to access company resources from their unmanaged devices.
Zero trust in AWS

One of the most common examples of zero trust in Amazon Web Services is how millions of people interact with the company's platform through its management console and APIs. These interactions are typically performed over a variety of private and public networks. Through the AWS Management Console, customers can easily interact with the company's web services.
The security of Amazon Web Services API infrastructure is not dependent on the reachability of its networks. Every single request that is signed through its API is authenticated and authorized at a rate of millions of requests per second.
The strength of Amazon Web Services' Transport Layer Security protocol, which is the cryptographic backbone of the company's API infrastructure, ensures that every request is properly secured.
Challenges in implementing zero trust architecture
Implementing a zero-trust security model can be a complex and challenging process, but it is becoming increasingly necessary as cyber threats continue to evolve.
Cultural shift
Implementing zero trust can be a daunting task due to the cultural shift required to adopt this approach. In traditional models, the perimeter of an organization is considered to be the initial line of defense in the fight against attacks. However, in a zero-trust system, all network activities are considered untrusted until they are proven otherwise.
Complexity
Various technical solutions, such as identity and access management (IAM), micro-segmentation, continuous monitoring, and network security, data security - are required to implement zero trust. It can be very time consuming and complex to implement, especially for large organizations.
Integration
Zero trust involves the integration of multiple security solutions, including firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, encryption, and security information and event management (SIEM) tools. Integrating these solutions can be challenging, especially for organizations with a mix of on-premise and cloud-based systems.
Cost
The cost of implementing zero trust can be prohibitive for organizations that need an upgrade or replace their existing security solution. Budget for hardware, software, and staffing can add up quickly, making Zero Trust a difficult option for some organizations.
User experience
Finally, implementing zero trust can have an impact on the user experience, especially for users who are accustomed to having unrestricted access to the network. For example, users may need to go through multiple authentication steps before gaining access to sensitive data and systems, which can be frustrating.
Implementing a zero-trust security model can be a complex and challenging process. Organizations need to be prepared for a cultural shift, technical complexity, integration challenges, cost, and a potential impact on the user experience.
Mad Devs about zero trust architecture
Here is Mad Devs’ approach to implementing zero trust through the main stages:
Assessment
The first stage in implementing zero trust is to assess your current security posture. Review your current network infrastructure, security policies, and processes to identify any potential vulnerabilities. This stage is critical in determining the extent of the zero trust implementation and the areas that need improvement.
Planning and design
Once you have assessed your current security posture, the next step is to plan and design your zero-trust architecture. Identify the systems, applications, and data that need to be protected, and design a secure environment that meets your organization's specific security needs.
Implementation
After the planning and design stage, the next step is to implement the zero-trust architecture. This involves deploying the necessary security technologies, such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and multi-factor authentication systems. Additionally, you will need to establish security policies and procedures that enforce zero-trust principles.
Monitoring and testing
Once the zero-trust architecture is in place, the next step is to monitor and test the system to ensure that it is functioning as intended. Don't forget about testing the security systems and policies to ensure that they are functioning correctly and that they are providing the necessary level of protection.
Continuous improvement
The final stage in implementing zero trust is to continuously improve the security posture. A critical step is monitoring the system on an ongoing basis and making changes as necessary to address new threats and vulnerabilities. This stage is essential in ensuring that the zero-trust architecture remains effective over time and that your organization remains protected from cyber threats.
For example, through Mad Devs' involvement, GuardRails was able to develop a secure app that would allow users to monitor their network's activity and identify potential issues. More about you can read in our case study.
To wrap up
Zero trust works by using a combination of security controls and practices to protect an organization's systems, applications, and data. By verifying every access request, using micro-segmentation, continuous monitoring, encryption, threat intelligence, and least privilege access, organizations can greatly improve their security posture and reduce the risk of a successful cyber attack.