Efficient data management has become crucial in today's data-driven world, particularly for laboratories where precision and accuracy are paramount. This is where laboratory information management software, or LIMS, steps into the spotlight. This article aims to introduce you to the world of LIMS, explain what it is, how it operates, and why it is becoming increasingly important to a wide range of industries.
We will discuss the complexities behind LIMS, shedding light on its multifaceted functionality and exploring the various sectors that harness its power. From pharmaceutical companies ensuring the quality of life-saving drugs to environmental agencies safeguarding our planet, LIMS plays a pivotal role in revolutionizing data management and transforming how organizations operate.
Discover how this technology shapes the future of data management and precision across various domains.
What is a LIMS
A laboratory information management system (LIMS) is a software solution designed for efficient sample and data management. LIMS enables labs to streamline workflows, integrate instrumentation, and handle samples and their related information effectively. It also facilitates the rapid generation of reliable results and provides comprehensive tracking capabilities, allowing for efficient data management across various experiments and over time.
What is LIMS used for
With the exponential growth of data in recent years, traditional methods like spreadsheets and paper-based records are inadequate for handling the volume of information. LIMS automates and optimizes workflows, and minimizes errors caused by manual data entry. Additionally, it helps laboratories comply with rigorous regulatory requirements and quality standards, all while reducing turnaround time.
How does a LIMS work
LIMS software can include some of the following features:
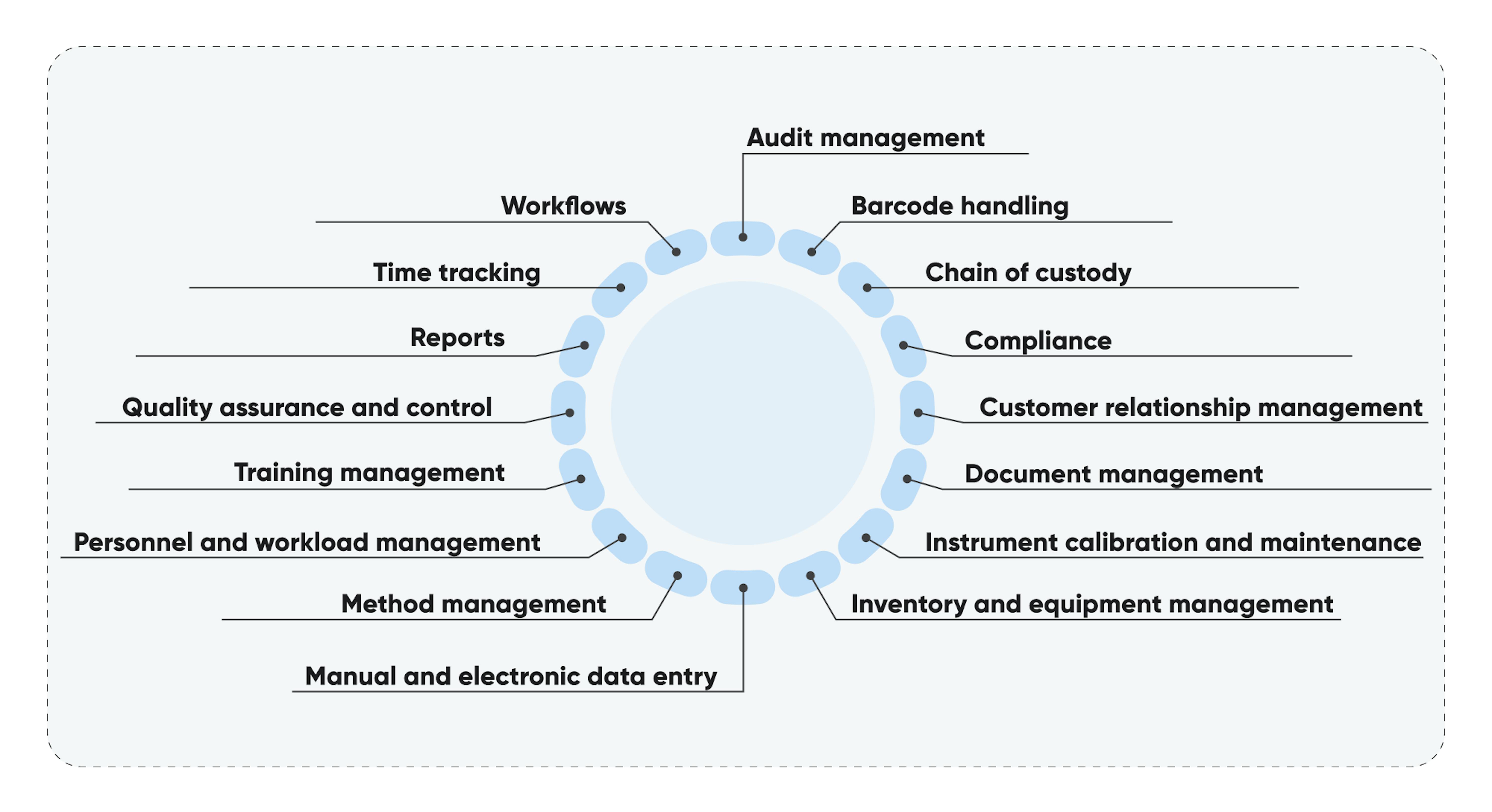
Audit management. Audit trails in LIMS are crucial for regulated laboratories and beneficial for any lab. They track actions, collaborators, and timestamps, enabling process oversight. LIMS automates audits, ensuring compliance and prompt detection of irregularities.
Barcode handling. LIMS replaces handwritten labels with barcodes, reduces errors, and improves data accuracy. Barcodes enhance sample tracking, provide more label information, and support barcode readers.
Chain of custody. In regulated laboratories, chain of custody (COC) tracking is crucial. LIMS with barcodes simplifies COC maintenance, ensuring effective inventory management and security configuration.
Document management. LIMS extends its capabilities to manage various data types, including documents, offering features like uploading, indexing, searching, and converting files, enhancing its utility.
Inventory and equipment management. Laboratories can benefit from LIMS in terms of time and effort saved in inventory management.
Manual and electronic data entry. LIMS provides lab technicians with user-friendly interfaces for efficient and customized data entry.
Method management. LIMS manages all laboratory processes, procedures (P&P), and methodology. All lab procedures are unified and arranged in this program. Additionally, LIMS provides lab technicians with instructions on how to perform current tasks.
Personnel and workload management. LIMS is a seamless extension of existing work processes. It helps with task scheduling, workload assignment, and maintenance planning, ultimately optimizing lab operations.
Training management. In addition to managing work schedules and maintaining employee records, LIMS provides a platform to schedule and plan training sessions for laboratory technicians.
Quality assurance and control. As mentioned before, LIMS manages and controls most lab processes, ensuring top-notch quality. It also conducts efficient quality checks on samples or products, automates logging, and swiftly extracts management information, guaranteeing comprehensive process control.
Reports. LIMS enables lab technicians to generate and schedule reports in custom formats to meet lab requirements or regulations. Once created, these reports can be instantly distributed to designated recipients for efficient information delivery.
Time tracking. Time-tracking feature records employee work hours, assisting with payroll management. Additionally, it can be applied for project-specific monitoring and assessing employee performance and task duration.
Workflows. LIMS automates task assignments, and sample tracking, and provides suitable equipment recommendations based on requirements. Overall, it simplifies lab workflows, and ensures efficient operations with minimal delays.
Regulatory compliance. Easy regulatory compliance of laboratory processes and procedures, including HIPAA, 21 CFR Part 11, ISO/IEC 17025:2017, ISO 15189, EU GDPR, ISO 20387, Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), Good Laboratory Practice (GLP), and Good Automated Manufacturing Practice (GAMP).
What are the benefits of LIMS
LIMS offers 4 key benefits in a laboratory setting.
Enhanced productivity
Efficiency is paramount in laboratories, where every detail counts. Cutting-edge technologies like LIMS have revolutionized the work environment and made tasks more efficient and less strenuous for lab technicians. LIMS offers user-friendly yet powerful features that empower lab technicians to work more productively, thereby motivating them to focus on essential tasks. It streamlines critical lab processes, saving time and improving overall work conditions.
Automation
LIMS simplifies and automates various labor-intensive tasks in the lab. For instance, it can automatically assign tasks to researchers and track sample locations in the workflow. Additionally, it manages laboratory inventory and equipment, reducing the burden on lab managers. LIMS also addresses instrument calibration and maintenance, ensuring smooth operations without the need for manual oversight.
Connectivity
LIMS is not isolated; it fosters connectivity. The software seamlessly integrates with other lab instruments and facilities through instrument integration and data management. This integration accelerates data transfer, enhancing efficiency and collaboration across different lab settings. LIMS connects with cutting-edge technologies like Microsoft HoloLens 2, creating innovative solutions like Holo4Labs, which combine augmented reality (AR) with lab management.
Cost reduction
LIMS improves efficiency and minimizes resource waste, such as paper usage. It digitalizes manual processes, reducing the need for physical document storage and archiving. Consequently, this software reduces costs associated with paper procurement, storage, and disposal while promoting eco-friendly practices.
📖 Want to know how Lean Six Sigma used in HealthTech to optimize processes, improve value and reduce waste? Read our new article "Lean Six Sigma: Bringing Value to Healthcare".
Who uses LIMS: 6 industry examples
LIMS, with its versatility and reliability, provides invaluable solutions for various industries. Whether it’s industrial production or criminology, LIMS ensures top-quality service while accommodating industry-specific requirements and regulations. Any organization with a laboratory can reap the benefits of implementing LIMS.
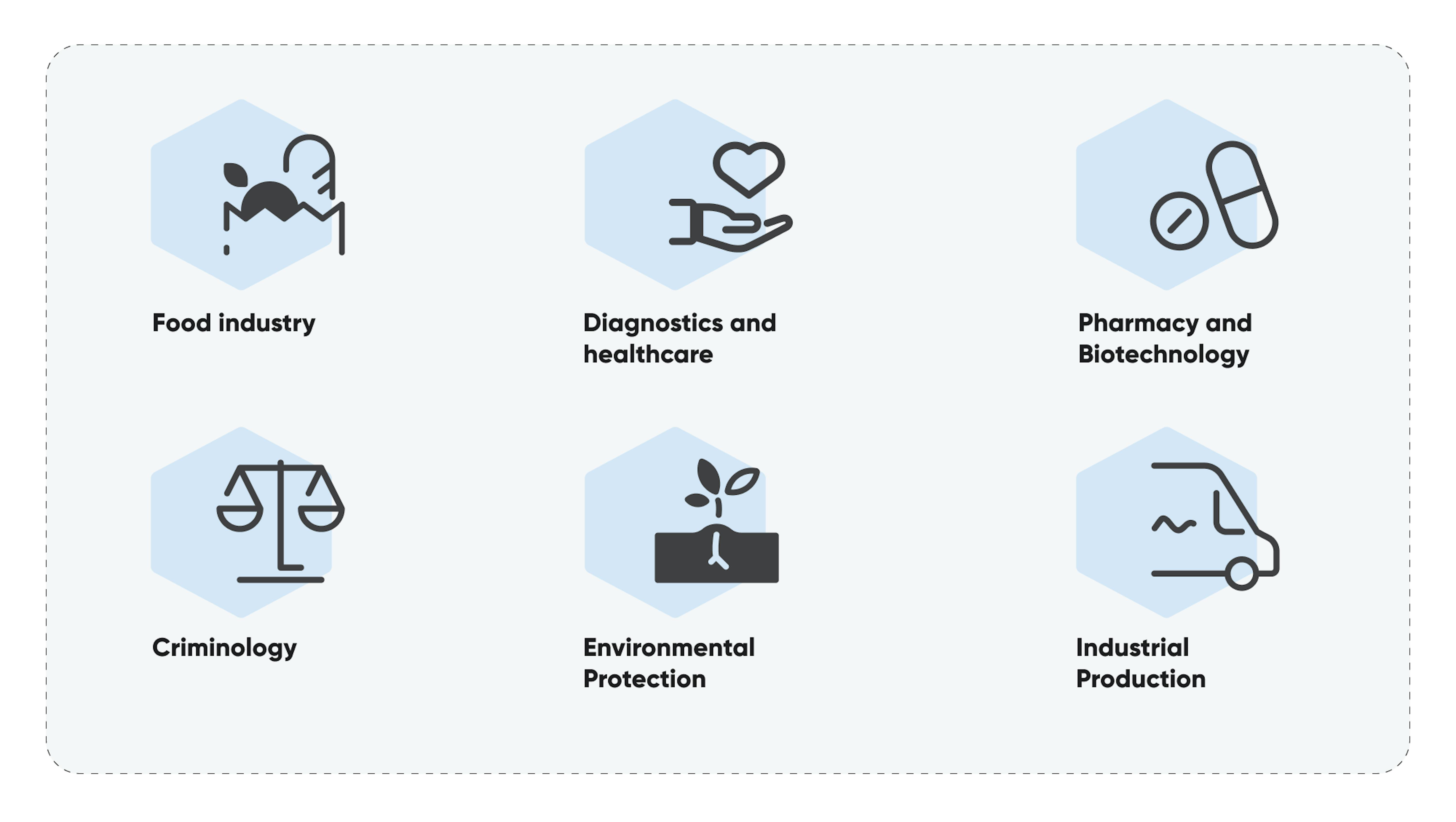
- Industrial production
Industries like chemicals, plastics, petroleum, and mining face the challenge of enhancing quality and productivity while adhering to strict regulations. LIMS helps streamline production processes, detect irregularities, and resolve issues. - Pharmaceutical and biotechnology
These types of companies need to develop new medicines and ensure the efficient production of existing drugs. LIMS optimizes drug manufacturing, reducing time to market. - Food industry
Food production demands rigorous control to meet safety protocols and regulations. LIMS aids in regulating processes, ensuring compliance, and testing new solutions. - Environmental protection
Businesses, both large and small, must comply with ever-changing environmental regulations. LIMS offers analysis technologies to minimize environmental risks and simplify regulatory compliance. - Criminology
Law enforcement agencies require modern tools and methods for crime investigation. LIMS is used in judicial and forensic laboratories, as well as field operations, to manage resources, results, and evidence efficiently. - Diagnostics and healthcare
LIMS implementation in healthcare laboratories enhances data throughput, research quality, and instrument integration.
Dive into the transformative realm of Generative AI. Discover how startups are no longer fun entertainment but essential tools for enterprises. Explore the market leaders, their role in addressing enterprise needs, challenges, and their future impact in our article.
Why is digital transformation important
In 2019, marked by the global pandemic, underscored the vital importance of digital transformation across industries for business survival. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have become critical tools, enhancing competition in the market. Timely, data-driven decisions are imperative for establishing market leadership.
Furthermore, the pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital work practices. Going digital enables remote work for individuals who do not require a physical presence at a specific location, ensuring ongoing productivity. In scientific companies, the use of a cloud-based LIMS that offers access from various devices, including tablets and smartphones — allows certain personnel to work safely from home rather than being placed in the office.
Most of the companies that upgraded or adopted LIMS come from the following industries: biotech/pharma, CRO/CMO, consumer products, chemicals, diagnostics, food and beverage, government, and others. Over 67% of respondents reported that their laboratories had at least one LIMS deployed across their enterprise. LIMS has provided several workflow efficiencies, including reports that 63% of LIMS users benefited from eliminating manual processes, 57% improved their sample management strategy, and 46% showed a significant increase in productivity within their laboratory environment.

Companies reported that the primary advantages gained from their LIMS deployment included:
- 61% benefited from the elimination of manual processes
- 57% achieved efficient sample management
- 50% gained efficiencies by having a single electronic data repository
- 46% reported increased productivity.
What is the point? To provide industry-driven insights and statistics to guide you on your digital transformation journey. In the modern world, it is important to adapt to modern market conditions and avoid the potential pitfalls surrounding LIMS implementations. Hence, digitally transform.
Digital transformation involves the incorporation of digital technologies and solutions into an organization's operations, strategies, and processes, fundamentally altering how it functions and provides value to its customers, employees, and stakeholders. This entails harnessing technologies like data analytics, cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), AI, and automation to stimulate innovation, boost efficiency, elevate customer experiences, and maintain competitiveness in the contemporary digital era.
Effective digital transformation implies the presence of the following 6 vital capabilities:
- Clear business strategy. Concentrate on particular areas that yield substantial value and craft a roadmap to initiate change.
- In-house digital talent. Form a team of digital experts to collaborate with business counterparts, encompassing talent acquisition, retention, and training initiatives.
- Scalable operating model. Set up a scalable operational framework to back cross-functional teams engaged in the transformation process.
- Distributed technology. Establish an atmosphere that enables teams to foster innovation, harnessing technology and automation capabilities independently.
- Accessible data. Guarantee teams across the organization can access up-to-date and dependable data, backed by robust governance practices.
- Adoption and change management. Begin by prioritizing adoption and change management initiatives, emphasizing iterative design, feedback loops, and continuous process enhancements from the outset.
Coordinated action across these areas is essential for successful digital transformation.
LIMS software brings the paperless culture to the labs. Progressive LIMS technologies have been designed to outgrow the current integration and innovation possibilities in labs.
Explore the dynamic world of biotechnology with a glance at its rich history, current market leaders, and the promising startups revolutionizing various industries.
What companies are doing it well
Digital transformation is essential for companies of all sizes and industries to remain competitive. Even well-established companies spanning various sectors can succeed in their digital transformation endeavors. Here are 3 illustrative examples of this phenomenon.

Labware LIMS is a validated lab management software with pre-configured workflows, enabling swift deployment. Both Labware LIMS and Labware SaaS LIMS provide robust features. They comply with MHRA, FDA, and WHO standards for GLP and GMP labs, offering different configurations within a compliant and validated environment. You can deploy Labware LIMS in the cloud or on-premises.
Solutions:
- ELN. The electronic laboratory notebook (ELN) enables automated experiments and procedure control, making it ideal for the guided execution of standardized testing methods (STMs) in research and quality control settings.
- Portable disease surveillance lab. The portable disease surveillance lab offers rapid testing for infectious disease outbreaks, integrates with LIMS for direct data tracking, and supports multi-target testing.
- Data analytics and AI. Labware provides customers with advanced data management options, including data science, AI, and machine learning, to gain a competitive advantage in handling high-volume and complex data.

LabVantage SaaS integrates LIMS, ELN, LES, and SDMS into a unified laboratory informatics suite. It efficiently manages samples with electronic worksheets through lab equipment (LE), eliminating paper records. LabVantage captures and enforces stepwise execution of lab tests while ensuring secure capture of instrument-related data files and results with SDMS. This simplifies data management, reduces bottlenecks, and ensures data integrity with flexible storage options.
Solutions:
- Configuration management and transfer. This feature allows you to manage and control changes to master data and LIMS configuration, collaborate with administration teams, and maintain an audit trail for documentation.
- LabVantage portal. This portal provides secure self-service access for external clients, automates service requests, and safeguards data in your LIMS database.
- LabVantage analytics. You can use the analytics tool to explore, analyze, and visualize lab and enterprise data, gaining control and making more informed decisions.

STARLIMS is a cloud-based laboratory management software that enhances quality and safety. This integrated platform incorporates ELN, SDMS, mobile features, and advanced analytics for insightful data. With its integrated solution, STARLIMS combines LIMS, ELN, and SDMS to streamline data collection and document management.
Solutions:
- SDMS. As part of the STARLIMS integrated solution, SDMS utilizes advanced technology to manage various documents, including SOPs and certificates of analysis.
- ELN. STARLINK ELN enhances lab efficiency and ensures workflow adherence with on-screen method instructions displayed alongside data entry.
Companies comparison
| LabWare | LabVantage | STARLIMS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product offerings | LIMS, ELN, sample management, quality management | LIMS | SDMS, ELN, Unified Solution |
| Pricing | Basic implementation for a small laboratory with 10 users might cost around $50,000 per year. A more complex implementation for a large laboratory with 100 users might cost around $250,000 per year. | Basic implementation for a small laboratory with 10 users might cost around $20,000 per year. A more complex implementation for a large laboratory with 100 users might cost around $100,000 per year. | Basic implementation for a small laboratory with 10 users and 10,000 monthly transactions might cost around $10,000 per year. A more complex implementation for a large laboratory with 100 users and 100,000 monthly transactions might cost around $500,000 per year. |
| Features | - Sample management - Data management - Workflow management - Inventory management - Instrument integration - Compliance tracking - ELN - Reporting and analytics | - Sample management - Data management - Workflow management - Inventory management - Instrument integration -Compliance tracking - ELN - Reporting and analytics | - Sample management - Data management - Workflow management - Inventory management - Instrument integration - Compliance tracking - ELN - SDMS - Reporting and analytics |
| Strengths | - Comprehensive feature set - Easy to use and configure - Scalable to meet the needs of laboratories of all sizes - Strong customer support | - Flexible and configurable - Strong focus on compliance - Good integration with other laboratory systems - Competitive pricing | - Comprehensive feature set - Strong focus on compliance - Good integration with other laboratory systems - Global reach and support |
| Industries | - Biobanking and Clinical - Cannabis and Hemp Testing - Compounding pharmacies - Contract services - Environmental - Food and Beverage - Forensics - Healthcare - Mining and Metals - Oil and Gas - Pharmaceutical - Process and Chemical - TIC | - Biobanking - Food and Beverage - Forensic Navigator - Oil and Gas - Pharma and Biotech - Public Health Labs - Medical Labs | - Pharmaceutical and Biotech - General Manufacturing - Contract Services - Molecular Testing - Biorepositories - Clinical Research - Environmental Sciences - Food and Beverage - Chemical, Petrochemical, and Refining - Public Health - Forensics |
Embark on a journey into the heart of Industry 4.0, where faster wireless tech and advanced data processing create unprecedented opportunities. Explore the definition of Digital Twins, working principles, limitless potential, and applications across various industries, including their transformative role in medicine.
Conclusion
After exploring the unique features of various LIMS software in this guide, you're now ready to make an informed decision. Some LIMS cater to various industries, while others specialize in specific fields.
To choose the right software, carefully assess your workflows and the capabilities of each option. Consider your team's characteristics, research design, industry, and overall work environment. Additionally, factor in your staff's skills and the implementation costs.
Modern labs handle vast amounts of data, highlighting the need for a centralized system like LIMS. It ensures consistency, meets user needs, and simplifies data management, workflow design, automation, and protocol sharing. With a clear understanding of your requirements, selecting the best LIMS software becomes straightforward.
You can contact us if you still have any doubts about what tools to choose or how to create your own.









