Analyze with AI
Get AI-powered insights from this Mad Devs article:
In the first article, we talked about how to log properly, and also when and where to use different types of levels. If you missed first part go check it out below link:
Log management in Go
This article is mostly about controlling your logs and finally, I wanted to show how to use logs (of level Error or higher) to take quick actions in case something bad happens.
How to log a log: approaches to control your logging
Now, your project might have only one package, yet, when it grows, the number of packages grows as well, so logging might become a little complicated. There are three basic approaches to how you might want to control your logging in a multi-package project.
The first one is to use just the default logger instance of Logrus everywhere. You can use it right out of the box referring directly to Logrus instance. Which you, therefore can control out of any package anytime.
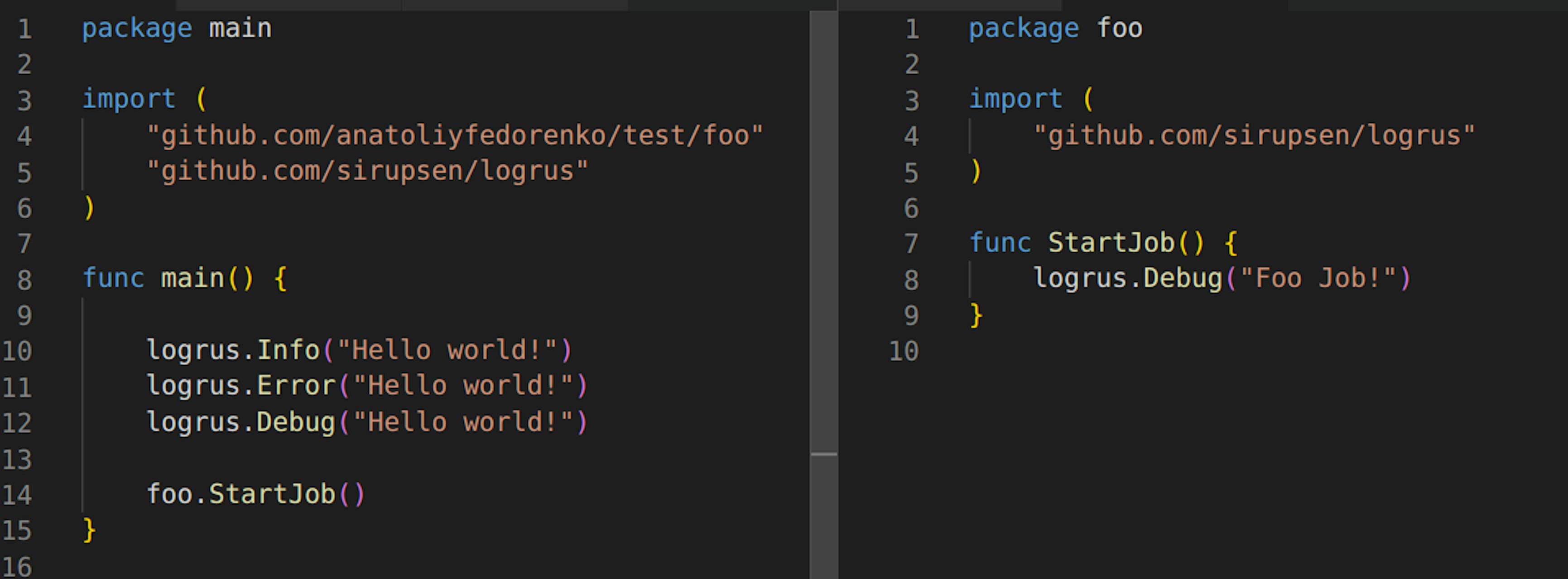
This produces the following results:

Changing logging level from Foo package will, therefore, have its effect on both packages:
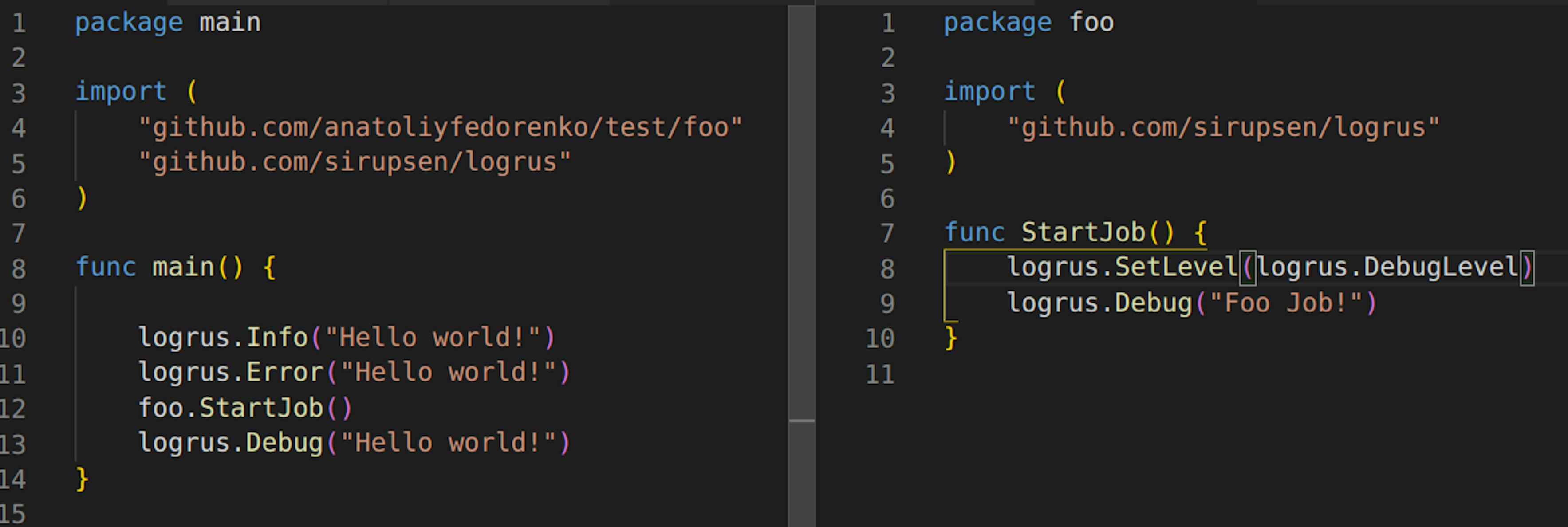

But of course, it would not affect any of the previous run code.
With this approach, I recommend using init() function to set up Logrus logger right ahead and therefore establish settings for all packages right away (and not change them further)
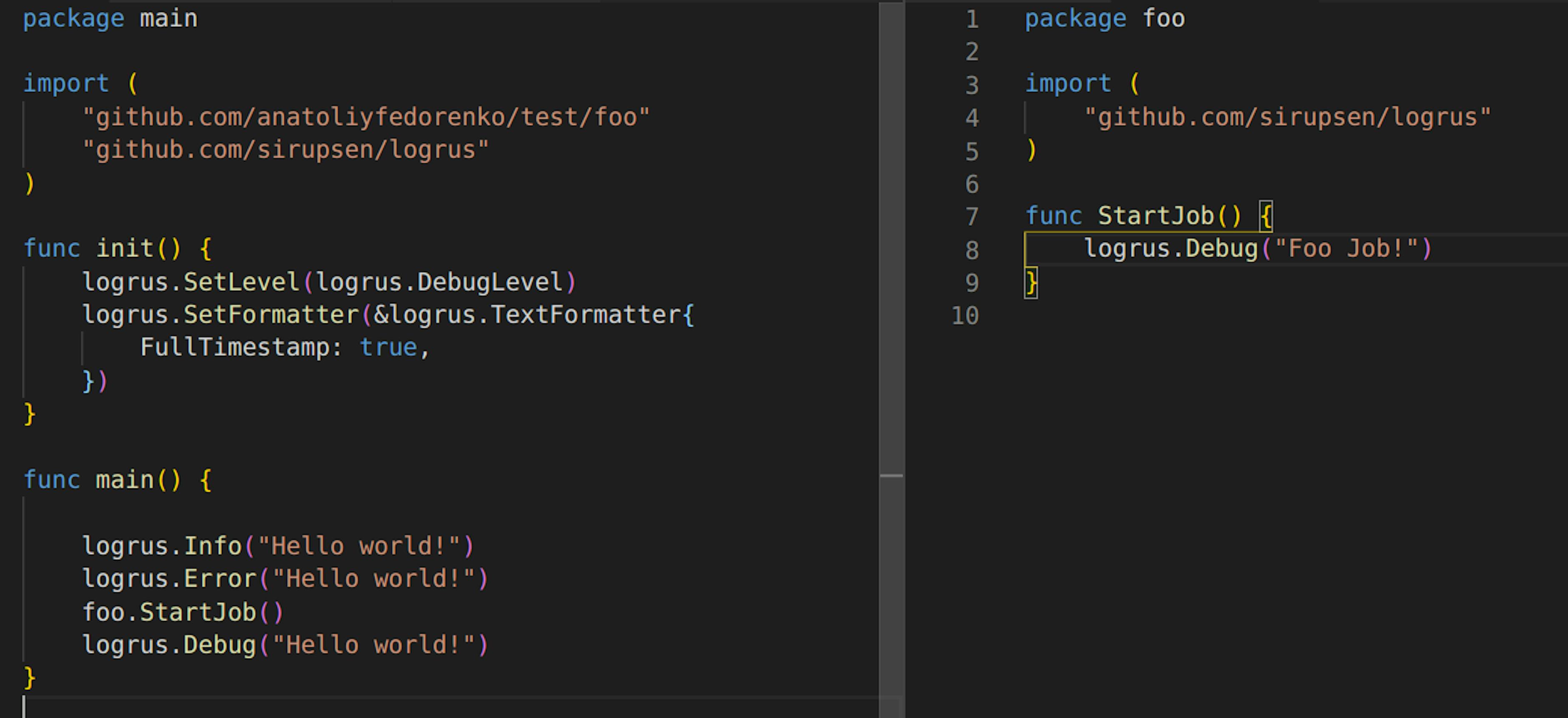
As a result, we see this:
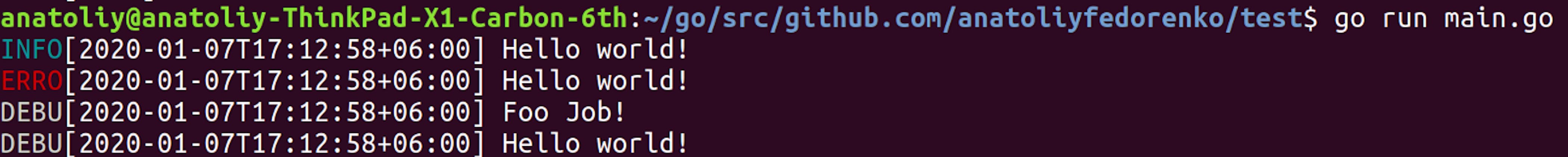
The second approach is you create one instance of a logger, update its log level, and then use this logger for all the packages within your project. This is not very much different from the previous example, yet, for many people, it looks more manageable and comprehensive.
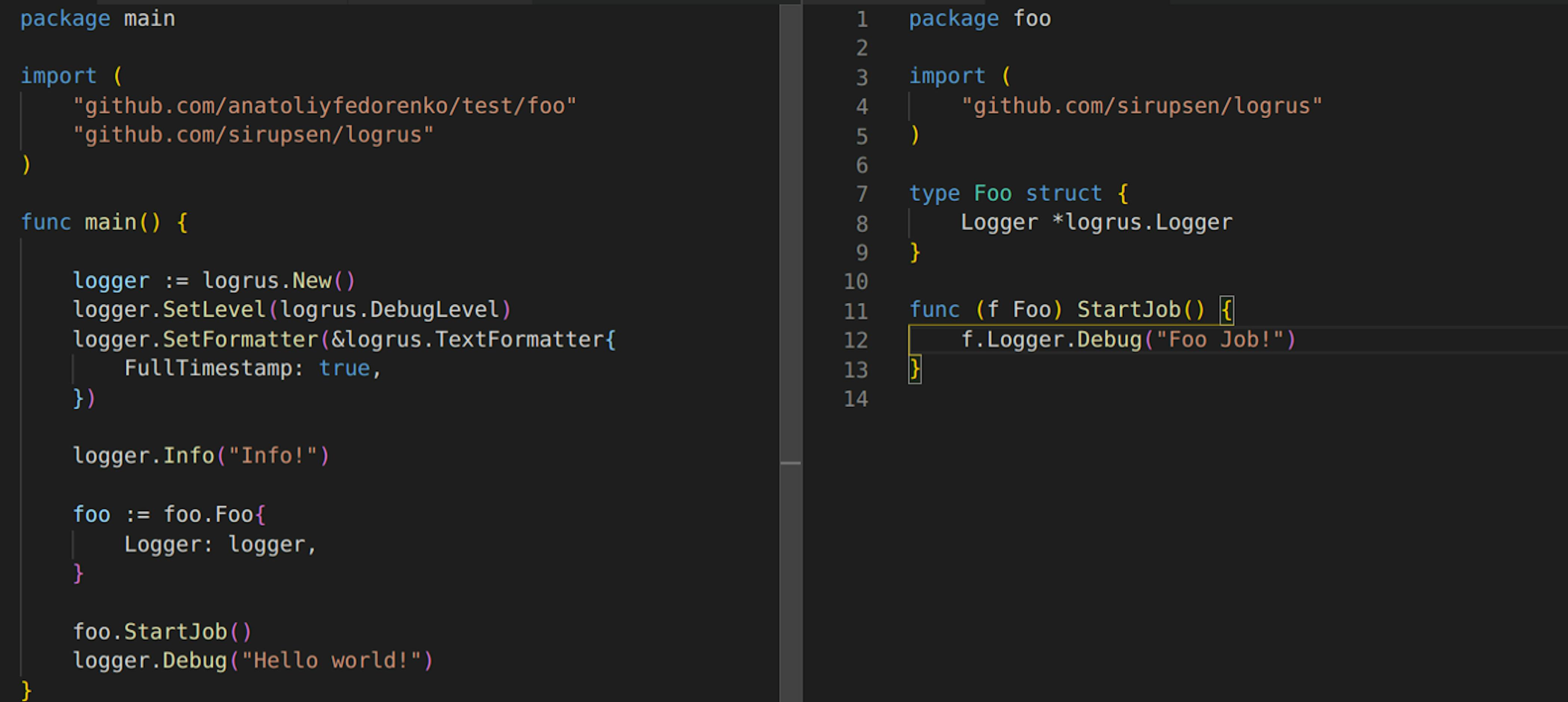

You might want to initiate separate loggers with separate logging levels since there are cases where you would like to see more logs from one package but avoid seeing more logs from other packages. With this approach you can do just that, yet, the configuration becomes a problem then. You either use yaml or json configuration files. In case you use environmental variables, there will be a lot of them… so, think twice
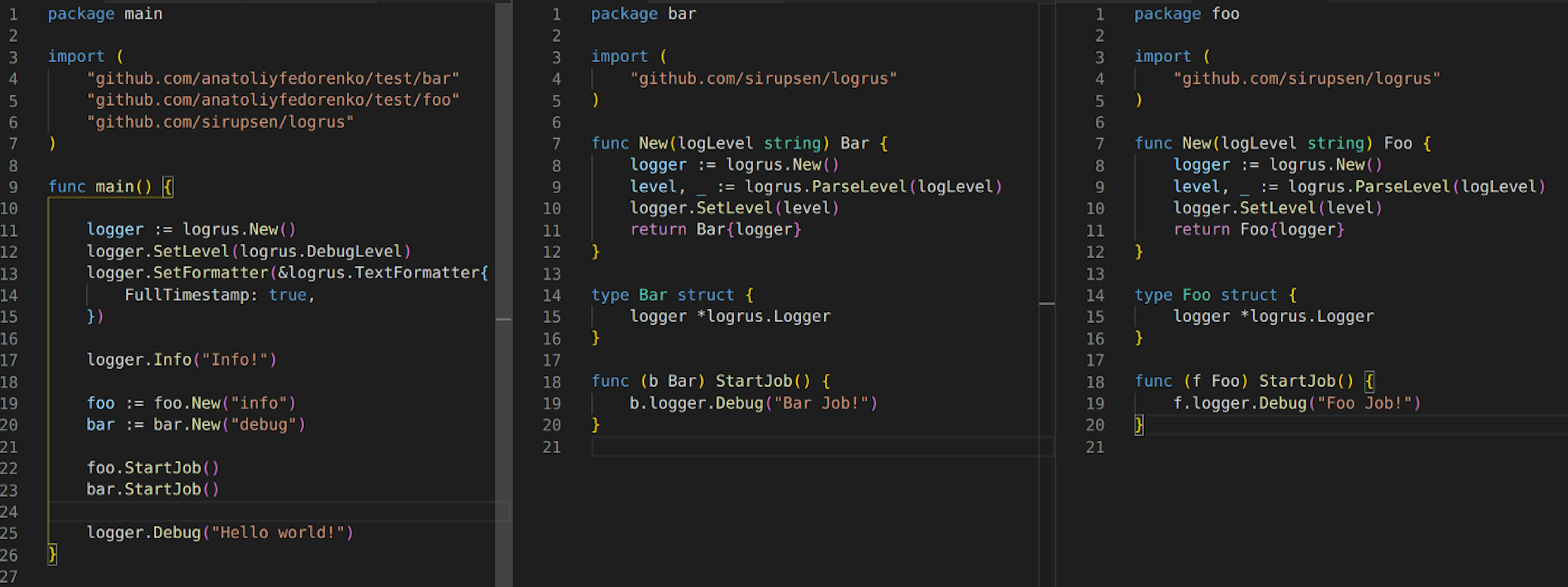
As a result, we have two packages with a different set of loggers and therefore different messages. Might be useful when we need more logs from one package and less from the other

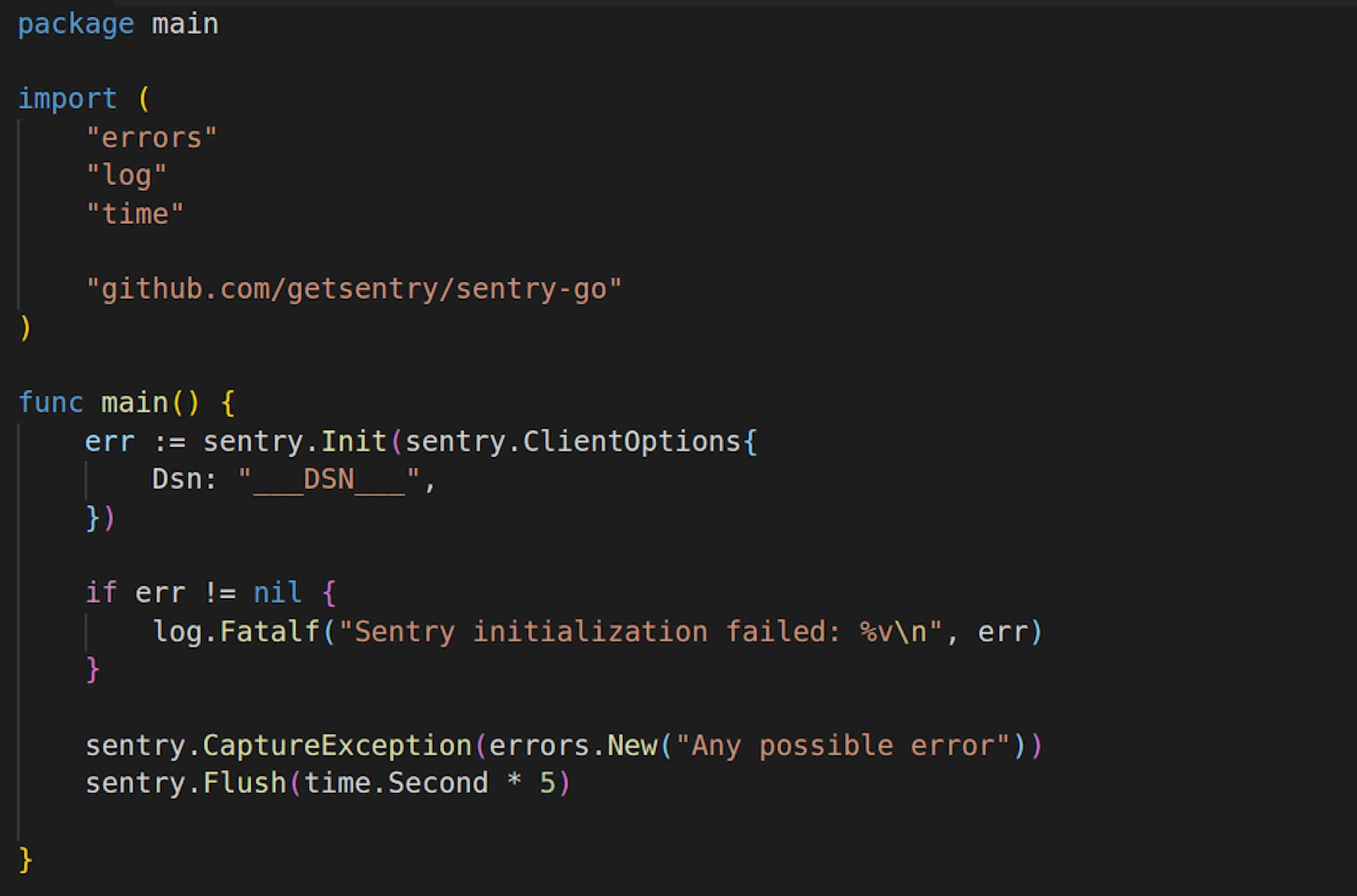
Logging by itself is great but not very useful. What if you want to be notified if something unexpected happens? You have "error" or "panic" logs, but not sure if you want to check log files each second to make sure nothing bad happened. This is where services like Sentry comes into play. Sentry has official SDK for Go which you can use to easily capture errors and other unexpected behavior of your code.
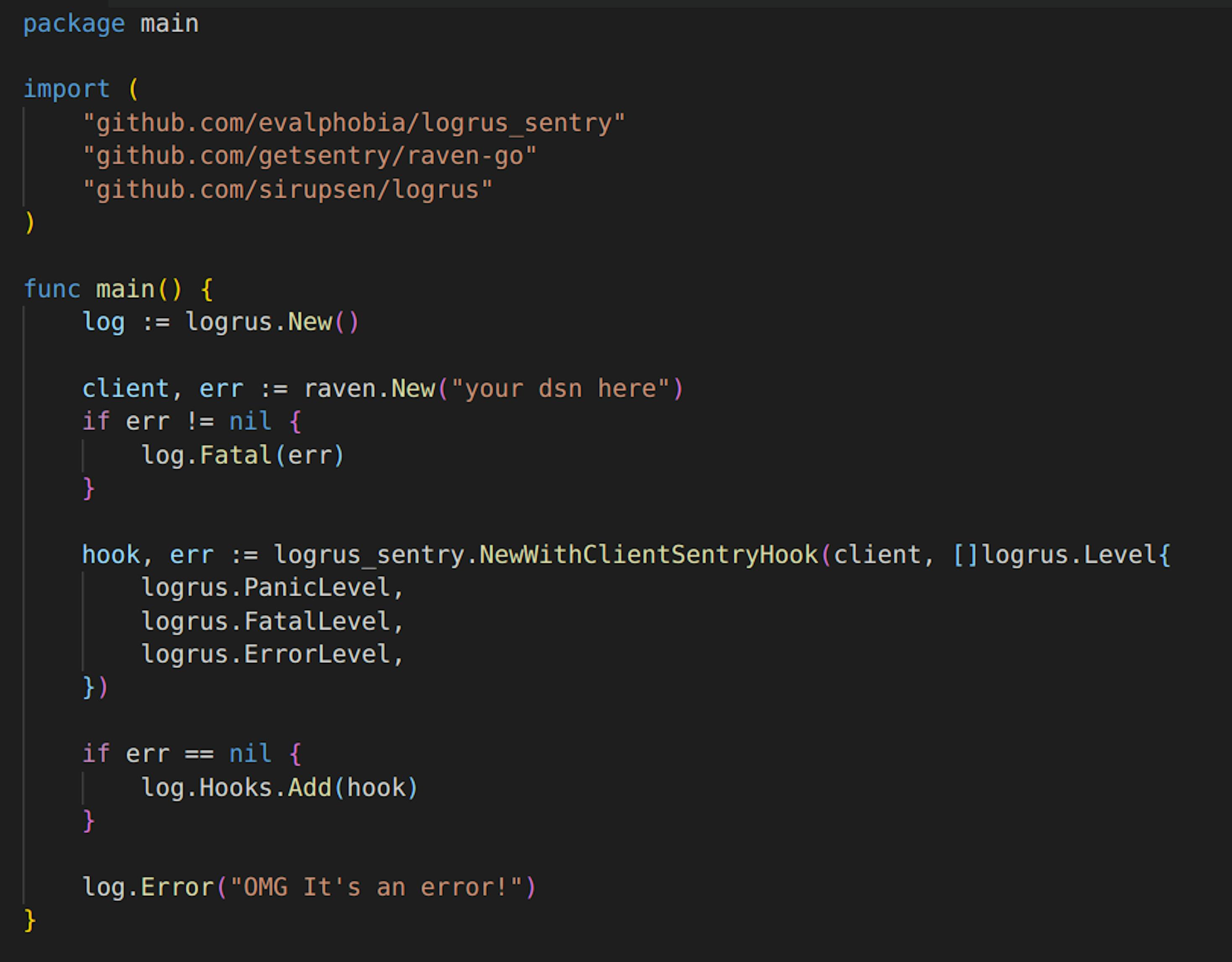
Personally I prefer to use Logrus Hooks and there is a very good Logrus hook for Sentry which helps to capture errors and other unexpected behavior right with Logrus without the need to wrap them with sentry.CaptureException method.
For more comprehensive information, please, read the following Datadog article about logging in Go which provides a lot of insides on logging in Golang with examples.











