Analyze with AI
Get AI-powered insights from this Mad Devs article:
To prepare for a SOC 2 audit, it is essential to understand the necessary steps you have to undergo. The absence of a clear checklist for SOC 2 compliance can make it challenging to assess your readiness before the actual audit.
Both free and paid tools are available to help you achieve SOC 2 compliance. This article explores various solutions suitable for different types of businesses to establish a network environment that aligns with SOC 2 standards.
Read this article to better understand how to initiate the SOC 2 audit preparation process, who should be involved, and what free and paid tools are available.
What is SOC 2
SOC 2, or Systems and Organization Controls 2, was established by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) in 2010. It offers auditors a framework to assess the operational effectiveness of an organization's security measures. This security framework primarily addresses customer data handling in cloud storage and aims to foster trust between service providers and their customers.
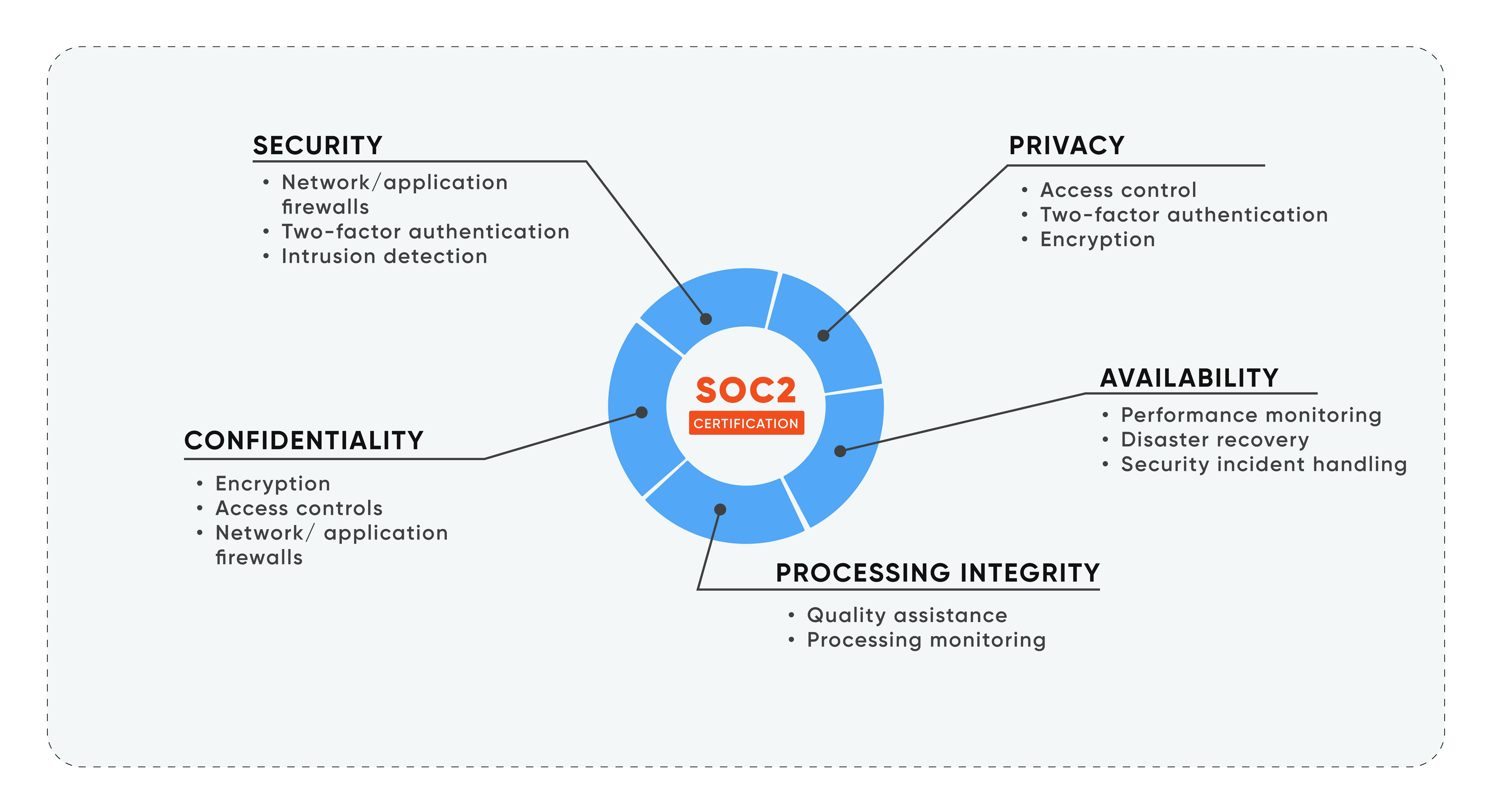
Unlike PCI DSS, which imposes stringent standards, each organization can customize its SOC 2 reports. Organizations design their controls by their unique business practices, aligning with one or more trust principles.
These internal reports offer essential insights into how your service provider handles data, benefiting you and regulators, business partners, suppliers, and others.
There are two types of reports:
- Type I assesses the design of a vendor's systems against relevant trust principles
- Type II evaluates the operational effectiveness of these systems.
Consider your objectives, budget, and timeframe when deciding between the two options. While a Type I report may be quicker to obtain, a Type II report provides higher assurance for your customers.
SOC 1 vs SOC 2
Both SOC 1 and SOC 2 are compliance standards regulated by the AICPA, but they have different goals. SOC 2 is not an upgrade to SOC 1. The table below compares SOC 1 and SOC 2.
| SOC 1 | SOC 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Assists a service organization in reporting on internal controls related to its customers' financial statements. | Aids a service organization in reporting on internal controls safeguarding customer data per the 5 Trust Services Criteria. |
| Control objectives | A SOC 1 audit encompasses handling and safeguarding customer information throughout business and tech processes. | A SOC 2 audit encompasses all permutations of the five principles. Some service organizations, for instance, focus on security and availability, whereas others adopt all five principles based on their operational nature and regulatory mandates. |
| Audit intended for | The Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) of the audited organization's management, external auditors, user entities (customers of the audited service organization), and CPAs responsible for auditing their financial statements. | Executives, business associates, potential clients, compliance supervisors, and external auditors affiliated with the audited entity. |
| Audit used for | User entities to help them understand how service organization controls impact their financial statements. | Supervising service organizations, supplier management strategies, internal corporate governance, risk management procedures, and regulatory monitoring. |
Why not SOC 3
SOC 3 is part of the SOC reporting framework, specifically designed to publicly distribute a service organization's audit report. It focuses on providing a high-level summary of the SOC 2 report without a detailed description of controls and test results. SOC 3 reports are meant for a wider audience, such as customers, vendors, and the general public.
There might be reasons not to use SOC 3 in certain situations:
- Insufficient detail. If you need more detailed information about a service organization's controls and security practices, SOC 3 may not provide the required level of detail. In such cases, a SOC 2 report might be more appropriate.
- Confidentiality concerns. SOC 3 reports are designed for public distribution, so if you have concerns about disclosing certain security information, SOC 2 or SOC 1 might be more suitable.
- Specific audit requirements. Some regulatory or contractual requirements might mandate using SOC 2 or other reports. In these cases, SOC 3 might not fulfill the necessary compliance obligations.
The choice between SOC report types depends on your specific needs, the level of detail you require, and any regulatory or contractual requirements that apply to your situation.
Who needs to be SOC 2 compliant
SOC 2 compliance is typically pursued by service organizations that provide services like data hosting, processing, or management. These organizations often seek SOC 2 compliance to assure their clients and partners that they have effective controls in place to protect sensitive data. Among the most common types of service organizations SOC applies to are:
- Software as a service (SaaS) companies provide programs, apps, and websites.
- Companies that provide business intelligence, analytics, and management services.
- Businesses that oversee, facilitate, or consult with finances or accounting practices.
- Organizations that provide customer management and other client-facing services.
- Managed tech and security service providers, including those that help with SOC 2.
Depending on whether your company fits into one of these descriptions or fits more broadly into one of these service organizations, you may need to comply with SOC. Despite SOC's focus on service organizations, other regulatory guidelines AICPA provides inside and beyond the SOC framework extend its protections to supply chains and beyond.
What is a SOC 2 audit, and how does it work
While security frameworks like ISO 27001 and PCI DSS have strict requirements, SOC 2 takes a different approach. Controls and attestation reports are customized for each organization, with companies designing their controls to align with their Trust Services Criteria (TSCs). TSCs are the 5 criteria that are used to evaluate an organization's security, availability, confidentiality, processing integrity, and privacy in a SOC 2 audit.
Following an independent auditor's assessment of SOC 2 requirements, a compliance report is generated to evaluate the company's adherence to standards. Regardless of the audit outcome, every organization that undergoes a SOC 2 audit receives a report.
What does the SOC 2 audit process look like
The SOC 2 audit comprises two phases: preparation and execution.
In preparation for the audit, there are several steps you should take before engaging a CPA.
Determine audit scope and objectives. Define the specific goals of the audit and identify which controls will fall under its scope. If you're uncertain which Trust Services Principles are relevant, collaborate with your auditor to clarify this. Once the scope is well-defined, begin documenting your policies.
Document policies and procedures. SOC 2 Type 2 audits necessitate comprehensive documentation of information security policies based on the Trust Services Principles. These documents will serve as the basis for the auditor's evaluation of your controls, so they must be clear and thorough. Depending on the number of principles and controls applicable to your organization, this step may require a dedicated team to assist.
Conduct a readiness assessment. With your policies meticulously outlined and documented for the auditor, conduct a readiness assessment to gauge your preparedness for the SOC 2 audit. This exercise essentially serves as a practice round before the official audit, allowing you to assess your policies and procedures and identify any weaknesses or risks in your framework.
Once you've prepared for the audit, your CPA will follow this SOC 2 audit checklist:
- Audit scope review. The auditor will initially review the audit scope to ensure it is well-defined.
- Project plan development. Using the established scope, the auditor will create a project plan and present an anticipated timeline for the audit.
- Security control testing. Subsequently, the auditor will test your controls, evaluating their design and operational effectiveness.
- Results documentation. The findings of the audit will be meticulously documented.
- Client report delivery. Finally, the auditor will furnish a comprehensive written assessment of your controls, culminating in a final opinion on the organization's adequacy in ensuring data security.
A SOC 2 audit report maintains validity for 12 months from the report issuance date. It is recommended that organizations conduct an annual SOC 2 audit to uphold ongoing compliance and strong security practices.
Which staff members support a SOC 2 audit
A SOC 2 audit is a significant endeavor that goes beyond the purview of your tech or security teams. In preparation for your SOC 2 audit, it is essential to consider the key individuals who should be engaged in the process and the specific roles that will be required.
- Executive sponsor
- Project manager
- Legal
- HR
- Tech or security team
- External consultant
What is the cost of a SOC 2 audit
A SOC 2 audit is a significant investment, encompassing time, financial resources, and workforce expenses. Beyond the audit process, personnel expenditures, tools, and training costs should be considered when calculating the comprehensive investment. In total, a 6-month SOC 2 audit may amount to approximately $147,000.
What tools can you use to prepare
You can use various tools to prepare a passage for SOC 2 compliance. There are free and paid options.
Free tools we recommend starting with
While working on one of our projects, we had to deal with SOC 2 compliance. In practice, we found that using a single tool was not very convenient, so among all the tools, we can highlight the following:
Scout Suite
It is an open-source tool for assessing the security posture of multi-cloud environments. Scout Suite utilizes cloud providers' APIs to collect configuration data for manual inspection and pinpoint potential risks. Instead of sifting through numerous web console pages, it offers an automated, clear view of the attack surface. Designed by security experts, it delivers a security-focused snapshot of the specific cloud account it assesses. Once it gathers data, you can conduct all the analysis offline.
Features:
- Supports Amazon Web Services
- Works with Microsoft Azure
- Supports Google Cloud Platform
- Alibaba Cloud (alpha) supported
- Works with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (alpha)
- Scout Suite is run through the CLI
Prowler
The open-source security tool that conducts assessments, audits, and various security best practices across AWS, GCP, and Azure. It is designed to continuously monitor, harden, respond to incidents, and be ready for forensics.
Prowler encompasses an extensive range of controls, addressing standards like CIS, NIST 800, NIST CSF, CISA, RBI, FedRAMP, PCI-DSS, GDPR, HIPAA, FFIEC, SOC2, GXP, AWS Well-Architected Framework Security Pillar, AWS Foundational Technical Review (FTR), ENS (Spanish National Security Scheme), and customizable security frameworks.
Features:
- Cloud auto-monitoring
- Security compliance verification
- Comprehensive cloud visualizations
- Remediation recommendations
- Agentless, fast integration.
Paid data verification tools
Solutions that support SOC 2 compliance, catering to startups, SMBs, and enterprise businesses aiming to establish a network environment aligned with SOC 2 standards.
Vanta
Vanta is a trust management platform that helps businesses automate compliance, streamline security reviews, and gain holistic risk visibility. It automates a significant portion of the work required for security and privacy frameworks, making audits more efficient. Vanta provides real-time monitoring, comprehensive reporting capabilities, and integrations to ensure a complete picture of the risk landscape.
| Key features | Pros | Deployments |
|---|---|---|
| - Identity lifecycle management - Single sign-on (SSO) - Multi-factor authentication (MFA) - Device management for Windows, Mac, Linux, and mobile devices - Risk assessments, conditional access, and audit logging. | - Cloud-based platform - No additional hardware - Centralized user management - Integration with other tools. | - On-premise and cloud deployments. |
Drata
It is a compliance automation platform offering automated SOC 2, HIPAA, GDPR, and risk management solutions. This tool helps organizations start with compliance, scale their governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) programs, and enhance their security and compliance efforts. Drata provides continuous monitoring, evidence collection, and risk assessment.
| Key features | Pros | Deployments |
|---|---|---|
| - One platform for all frameworks. - Continuous control monitoring. - Evidence collection and testing. - Customizable controls. - Compliance expertise and support. | - Automated compliance management - Continuous compliance - Easy to use - Scalable | - On-premise and cloud deployments |
JumpCloud
It provides a no-cost SOC 2 compliance tool that ensures data security and privacy through internal control validation. While the tool is free, JumpCloud also offers paid plans with additional features and support. It helps organizations implement and maintain the necessary controls to meet SOC 2 requirements.
| Key features | Pros | Deployments |
|---|---|---|
| - Identity lifecycle management - Single sign-on (SSO) - Multi-factor authentication (MFA) - Device management for Windows, Mac, Linux, and mobile devices - Risk assessments, conditional access, and audit logging. | - Cloud-based platform - No additional hardware - Centralized user management - Integration with other tools | - On-premise and cloud deployments |
Sprinto
Sprinto is a robust platform for automating security compliance tailored to the needs of rapidly expanding, cloud-based businesses. It features powerful and straightforward architecture that automates and oversees end-to-end compliance tasks. Sprinto is compatible with various frameworks such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, ISO 27017, FCRA, CIS, OFDSS, NIST, CCPA, CSA Star, and even custom frameworks. With Sprinto, you can continuously monitor cloud controls, detect non-compliant activities, pinpoint unusual behavior, trigger corrective actions, and efficiently gather audit evidence to stay ahead of your compliance obligations without any disruption.
| Key features | Pros | Deployments |
|---|---|---|
| - Vulnerability & incident management - Role-based access controls - Tiered remediation - Baked in MDM (mobile device management) | - Scalable compliance programs - 100+ integrations supported - Audit-friendly - Ready to use documents and policy templates | - On-premise and cloud deployments |
Conclusion
In contrast to other frameworks, SOC 2 doesn't offer a predefined set of requirements for businesses to follow to attain certification. Instead, it evaluates the efficiency of controls based on the 5 Trust Service Criteria. This can add complexity to the certification process. However, using SOC 2 software can streamline this journey and become especially helpful for newcomers.













