Cloud computing is the process of delivering computing services (software, databases, servers and networking) over the Internet. It allows you to save money on operating costs and provide better, flexible resources. As a result, it’s widely considered as the most cost-effective method of delivering computing services.
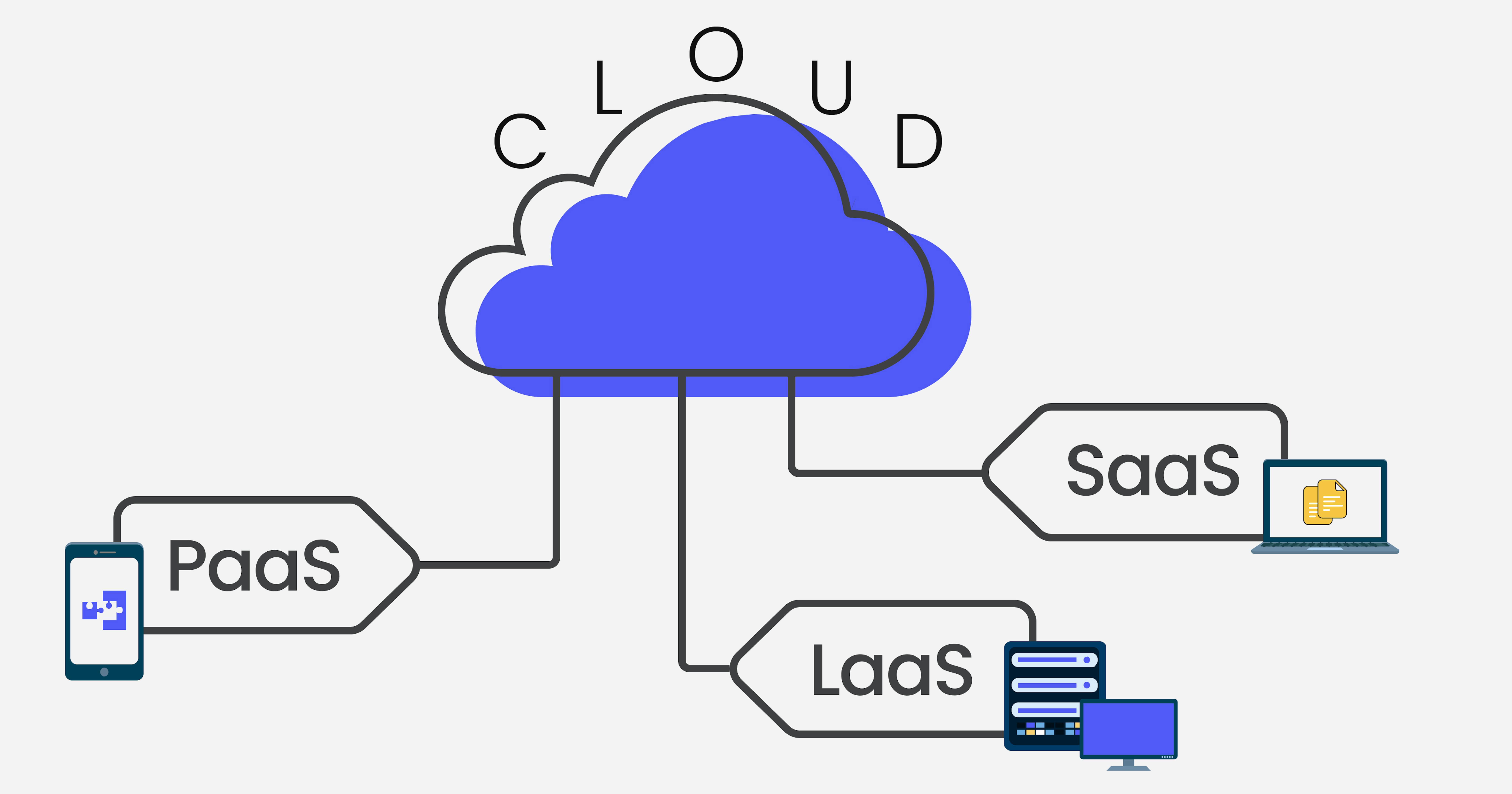
Most cloud computing services are divided into three broad classifications: infrastructure as a service, platform as a service, and software as a service. Understanding these terms simplifies the process of implementing and managing cloud computing.
Move to Cloud
The rapid emergence and evolution of digital businesses have caused many companies to question their current approach to doing business. Modern cloud solutions help organizations manage the complexity of today's digital world. Instead of being limited by their existing infrastructure, they can now respond quickly to changes and opportunities.
When a company moves its infrastructure to the cloud, it means that its data is stored offsite. The cloud computing provider manages the entire operation of the infrastructure. So, the cloud allows you to get all the resources you need without having to spend large amounts of money on hardware and support. It eliminates the need for expensive hardware and software updates each year. It also allows you to plan for the exact resources that you need to get started.
For example, Amazon Web Services is a Cloud computing provider that owns and maintains the hardware that enables its customers to run their applications.
So, when you seriously think about moving to the cloud, check these three cloud computing services. And we start with the most basic.
Infrastructure as a Service
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model that includes all the basics: server infrastructure, communications, storage, etc. Instead of maintaining your own IT infrastructure, you lease the cloud and the provider takes care of the maintenance.
What are the benefits of IaaS:
- Data is located in the provider's data center, where it is protected by security systems at the physical and software levels
- Saving the budget by transferring infrastructure costs to the provider
- Easily scale as your company grows
IaaS is the basis on which the company's software solutions are built. The IaaS provider provides fewer services than subsequent models. Depending on the needs of the company, this can be a plus. If you have your own strategy for developing IT solutions, this model will provide the greatest freedom to implement it. On the basis of IaaS, both individual applications and all IT tools of the company are deployed - ERP systems, terminal servers, remote offices, databases, etc.
Administration and monitoring of the IaaS system are implemented using a virtual interface. Here you manage the IaaS configuration, add pre-installed software, and connect additional services
What is PaaS (Platform as a Service)?
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) is a service model in which a provider offers a platform for developing and deploying applications with predefined settings. For example, a platform can be a mail server, a database management system, a web server, a development and testing environment, a backup server, etc.
Benefits of PaaS:
- The PaaS service provider is responsible for software updates, fixes, and maintenance
- The development, test, and deployment infrastructure is fully managed by the PaaS provider
- A client does not need to have his own hardware and software - everything needed is provided by the provider
PaaS is similar in many ways to IaaS, but the PaaS provider's customers do not have the ability to scale their infrastructure. That is, for example, the user cannot turn off unused capacities. The difference between IaaS and PaaS is that in a platform-as-a-service model, you get the compute infrastructure and solution stack, but you don't affect the platform configuration.
An important plus of the PaaS model is the standardized toolkit for developers. For example, it can greatly facilitate the work of a team that is busy with one project.
PaaS provides less freedom than IaaS, but it also eliminates the need to deal with tasks that the provider has already decided. Choosing between IaaS and PaaS is a matter of whether these solutions meet the needs of the business.
Examples of PaaS solutions: Google App Engine, IBM Bluemix, etc.
SaaS is an excellent choice if the provided service solves the assigned tasks because you just have to apply ready-made solutions
SaaS (Software as a Service) is
SaaS (English Software-as-a-Service) - the software as a service, implies the use by the client of applications deployed on the provider's platform. SaaS is a simple thing that you most likely use in your daily life. The customers of the SaaS service model are often end-users such as email services, online movie platforms, small cloud file storage, instant messengers, etc. Social media also operates on a SaaS model.
Enterprise customers of SaaS providers use video conferencing applications, ERP and CRM systems, business process automation systems, project management, and time management applications, e-mail services, etc.
The most familiar examples of Saas for you: Gmail, Jira, WordPress.
SaaS is an excellent choice if the provided service solves the assigned tasks because you just have to apply ready-made solutions. If you need a specialized approach that requires you to develop your own tools, prefer one of the two models above.
So which service model should you choose in the end?
Choosing a cloud service model is not a difficult task if you understand the capabilities and needs of the company.
IaaS is a solution for deploying systems and applications from scratch, so this solution will be of interest to corporate clients. IaaS startups and businesses often choose IaaS because of its relatively low cost and fast scaling up as the company grows.
PaaS provides cloud resources and a set of development tools. A pre-configured platform is a convenient solution if a company needs to solve a specific problem and the provider has all the necessary tools.
Finally, SaaS is a turnkey product that is developed, hosted, and maintained by a provider. The customers of such solutions are private users and corporate clients. Within the SaaS model, both messengers and CRM systems are provided.
The cloud is at the heart of these models, and the difference between them lies in the software add-ons. The choice of a service model is a question of how well these add-ons meet the company's objectives. If your task has already been solved by the provider's package of services, choose SaaS. If the provider does not have a ready-made solution but has the necessary tools, your choice is PaaS. If a company needs raw computing power to deploy its own solutions, IaaS is here for you.
Here, we provide you a table to ease your choice:

To wrap up
Cloud computing is helping developers and IT departments to focus on what they do best, without the need for additional work. As a result, many companies are choosing to use cloud computing instead of traditional means of managing their infrastructure.
Regardless of the type of cloud computing service that you use, one thing is clear: large amounts of data will always move back and forth between the providers' data centers and the end-users.










