[Guide: Setting Up OpenID Connect in AWS]
When setting up CI/CD, you need access to your cloud provider. Authenticating via access key and secret key is not a recommended practice. For such scenarios, AWS provides the OpenID Connect service. Let's explore how to configure OpenID Connect for two of the most popular CI/CD services: GitHub Actions and GitLab CI.
Configuring OpenID Connect in AWS for GitHub Actions
1. Create Identity providers:
- Navigate to the AWS console and select IAM.
- Choose Identity providers.
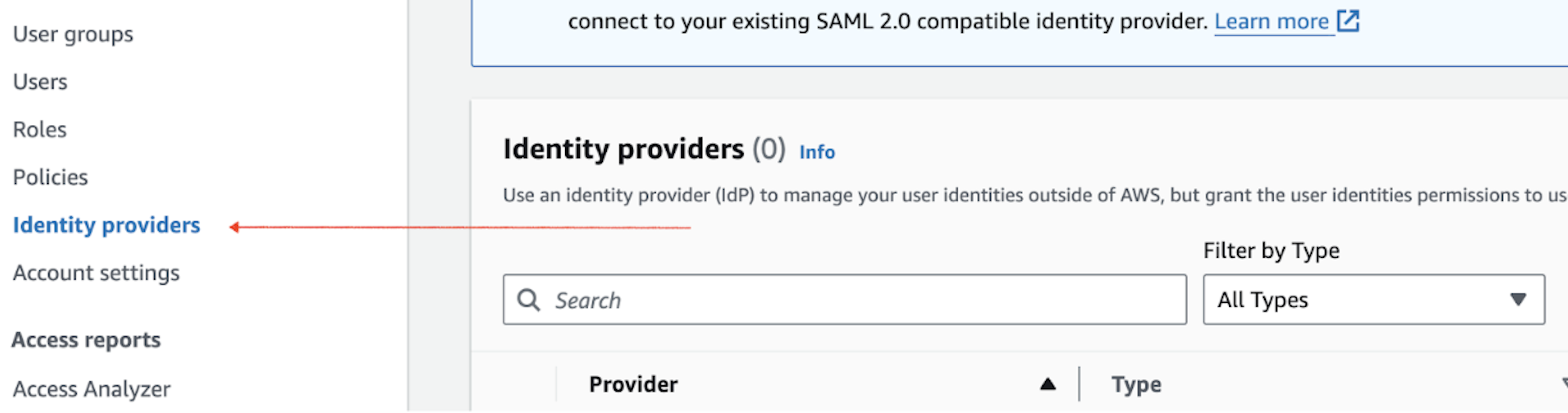
- Click Add provider -> OpenID Connect.
- In Provider URL, enter https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com and click Get thumbprint.
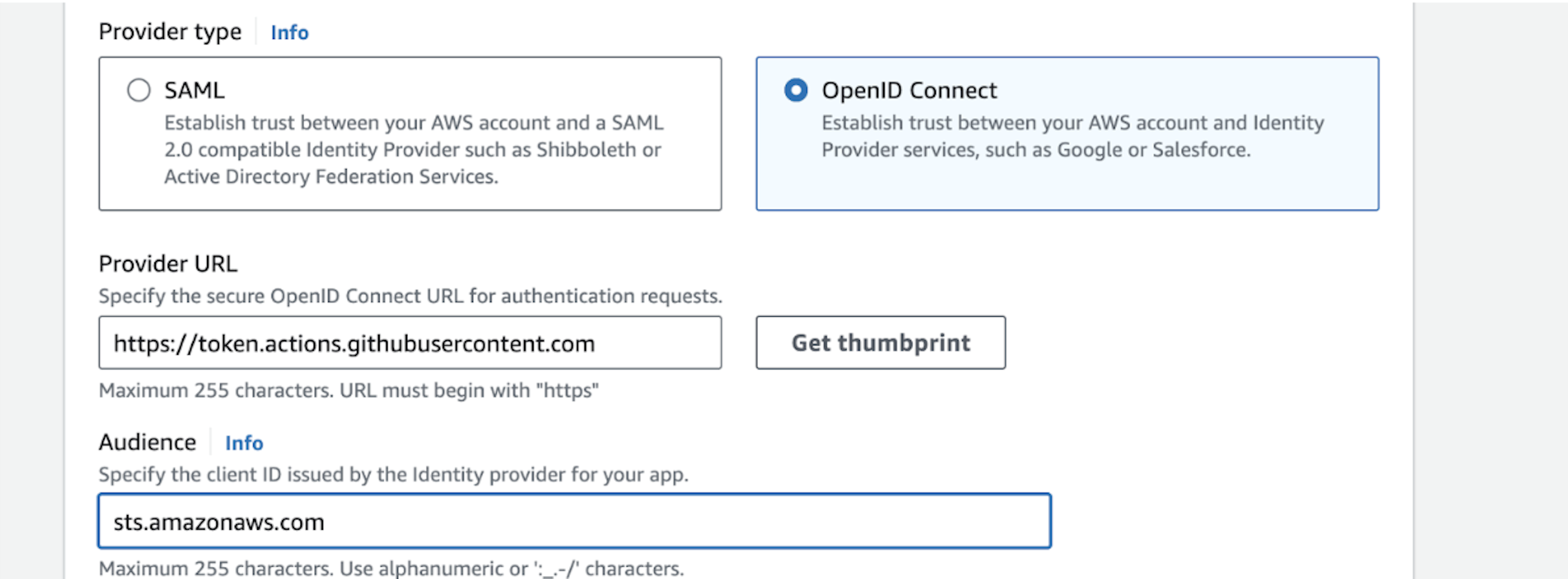
- In the Audience field, enter sts.amazonaws.com
- Create a new provider by clicking Add provider
2. Create a new role:
- Go to Roles
- Select Create role
- Choose Custom trust policy
- Edit the trust policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "ARN"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"token.actions.githubusercontent.com:aud": "sts.amazonaws.com",
"token.actions.githubusercontent.com:sub": [
"repo:ORG_OR_USER_NAME/REPOSITORY:ref:refs/heads/main"
]
}
}
}
]
}For example repository at https://github.com/vitaliimd/landing-page:
ARN - ARN of the created provider.
ORG_OR_USER_NAME - vitaliimd
REPOSITORY - landing-page
Click Next and add Permissions policies to the created role (e.g., AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess).
Create a GitHub workflow:
name: AWS example workflow
on:
push
env:
AWS_REGION : "us-east-2"
permissions:
id-token: write # This is required for requesting the JWT
contents: read # This is required for actions/checkout
jobs:
S3BuketList:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Git clone the repository
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: configure aws credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v1
with:
role-to-assume: ${{ secrets.ARN_ROLE }}
role-session-name: ci-cd
aws-region: ${{ env.AWS_REGION }}
# List bucket in AWS s3
- name: AWS S3 Ls
run: |
aws s3 lsARN_ROLE - Add the ARN of the previously created role to GitHub secrets.
Configuring OpenID Connect in AWS for GitLab CI
Navigate to the AWS console and select IAM.
Choose Identity providers.

Click Add provider -> OpenID Connect.
In Provider URL, enter https://gitlab.com and click Get thumbprint.
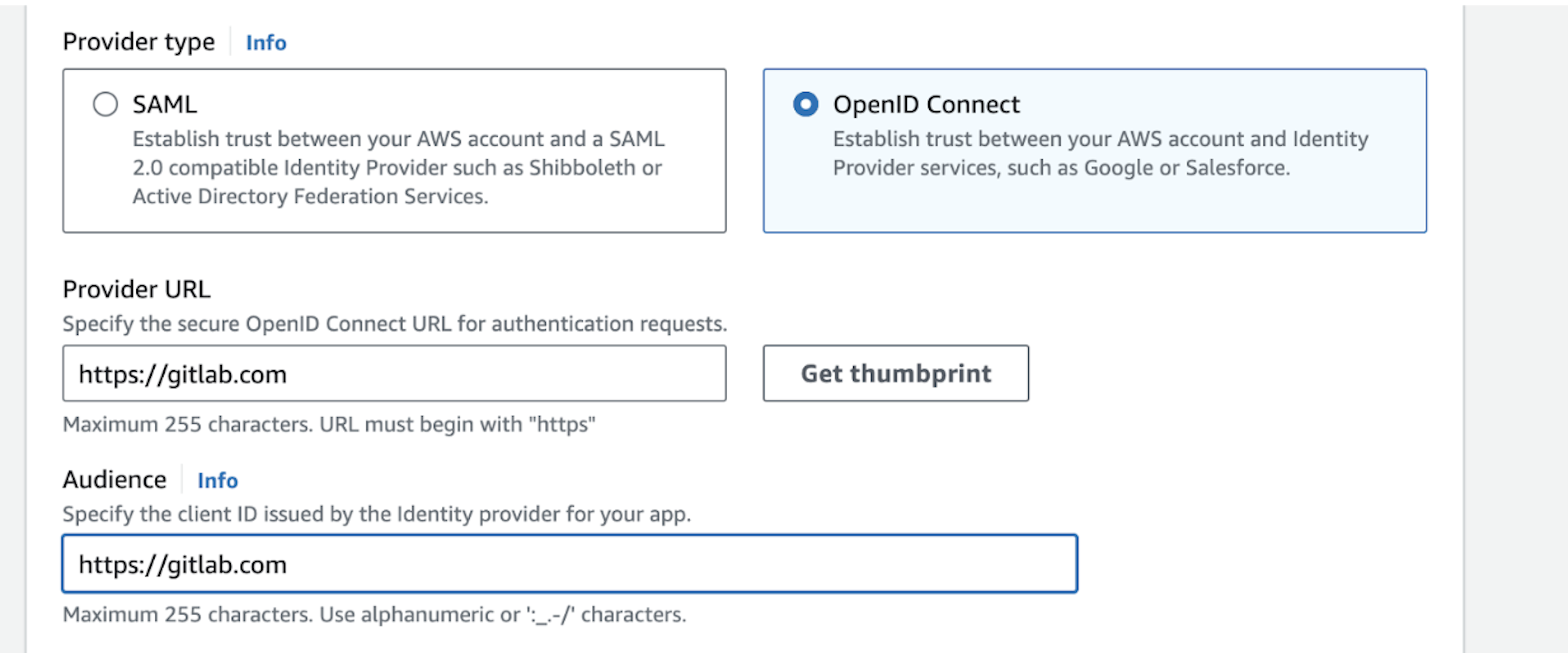
In the Audience field, enter https://gitlab.com.
Create a new provider by clicking Add provider.
Create a new role:
Go to Roles.
Select Create role.
Choose Custom trust policy.
Edit the trust policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": {ARN}
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"gitlab.com:aud": "https://gitlab.com"
},
"StringLike": {
"gitlab.com:sub": "project_path:{ORG_OR_USER_NAME}/{REPOSITORY}:ref_type:branch:ref:main"
}
}
}
]
}For example repository at https://gitlab.com/vitaliim1/test:
ARN - ARN of the created provider.
ORG_OR_USER_NAME - vitaliim1
REPOSITORY - test
Click Next and add Permissions policies to the created role (e.g., AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess).
Create a .gitlab-ci.yml:
services:
- name: docker:dind
entrypoint: ["env", "-u", "DOCKER_HOST"]
command: ["dockerd-entrypoint.sh"]
variables:
DOCKER_HOST: tcp://docker:2375/
DOCKER_DRIVER: overlay2
DOCKER_TLS_CERTDIR: ""
S3BucketList:
image:
name: amazon/aws-cli
entrypoint: [""]
variables:
AWS_PROFILE: oidc
before_script:
- mkdir -p ~/.aws
- echo "${CI_JOB_JWT_V2}" > /tmp/web_identity_token
- echo -e "[profile oidc]\nrole_arn=${ARN_ROLE}\nweb_identity_token_file=/tmp/web_identity_token" > ~/.aws/config
script:
- aws s3 ls
only:
refs:
- mainARN_ROLE - Add the ARN of the previously created role to GitLab CI/CD variables.
In this guide, we explored the process of setting up OpenID Connect (OIDC) in AWS for two popular CI/CD services, GitHub Actions and GitLab CI. By configuring Identity Providers and Roles in AWS IAM, and integrating them with GitHub Actions and GitLab CI workflows, we enhance security and move away from the use of access key and secret key authentication. This OIDC-based approach ensures a more robust and secure authentication mechanism for your CI/CD pipelines, promoting best practices in cloud security.
